OpenTelemetry Go AWS Lambda Instrumentation
AWS Lambda is a serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. By instrumenting your Go Lambda functions with OpenTelemetry, you gain visibility into execution times, cold starts, and downstream service calls.
How Lambda Execution Works
Lambda runs your code in isolated containers that scale automatically. When there are no incoming requests, Lambda freezes idle containers. This freeze/thaw behavior has important implications for telemetry:
- Frozen state: All processes pause, including background flush timers
- Unpredictable timing: Containers can remain frozen from seconds to hours
- Data loss risk: Buffered telemetry may never be sent if not flushed before freeze
The solution is to flush telemetry data synchronously before each Lambda invocation completes.
Installation
Install the OpenTelemetry AWS Lambda instrumentation package:
go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda
For AWS resource detection and X-Ray propagation support:
go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/detectors/aws/lambda
go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda/xrayconfig
go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/propagators/aws/xray
Basic Usage
The minimal API for instrumenting a Lambda function:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda"
)
type Event struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
}
func HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, event Event) (string, error) {
return fmt.Sprintf("Hello %s!", event.Name), nil
}
func main() {
lambda.Start(otellambda.InstrumentHandler(HandleRequest))
}
Warning: This minimal example uses the default TracerProvider and omits WithFlusher. Spans will be lost when Lambda freezes the container. Use the complete setup below for production.
Complete Setup with Uptrace
For production, configure a TracerProvider with flushing to prevent data loss:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
"github.com/uptrace/uptrace-go/uptrace"
lambdadetector "go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/detectors/aws/lambda"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel"
)
type Event struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
}
var tracer = otel.Tracer("lambda-handler")
func HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, event Event) (string, error) {
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, "process-event")
defer span.End()
// Your business logic here
result := fmt.Sprintf("Hello %s!", event.Name)
return result, nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Configure OpenTelemetry with Uptrace
uptrace.ConfigureOpentelemetry(
// Use UPTRACE_DSN environment variable
uptrace.WithServiceName("my-lambda-function"),
uptrace.WithServiceVersion("1.0.0"),
// Add Lambda resource detector
uptrace.WithResourceDetectors(lambdadetector.NewResourceDetector()),
)
defer uptrace.Shutdown(ctx)
tp := uptrace.TracerProvider()
lambda.Start(otellambda.InstrumentHandler(
HandleRequest,
otellambda.WithTracerProvider(tp),
otellambda.WithFlusher(tp), // Flush spans after each invocation
))
}
Configuration Options
The otellambda.InstrumentHandler function accepts several options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
WithTracerProvider(tp) | Custom TracerProvider for creating spans |
WithFlusher(f) | Flushes telemetry after each invocation (required for Lambda) |
WithPropagator(p) | Context propagator for distributed tracing |
WithEventToCarrier(fn) | Extract trace headers from custom event types |
WithTraceAttributeFn(fn) | Add custom attributes from event data |
AWS X-Ray Integration
If you're using AWS X-Ray for tracing, use the xrayconfig package for recommended settings:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda/xrayconfig"
)
type Event struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
}
func HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, event Event) (string, error) {
return fmt.Sprintf("Hello %s!", event.Name), nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Create TracerProvider with X-Ray configuration
tp, err := xrayconfig.NewTracerProvider(ctx)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer tp.Shutdown(ctx)
// WithRecommendedOptions configures X-Ray propagator and resource detector
lambda.Start(otellambda.InstrumentHandler(
HandleRequest,
xrayconfig.WithRecommendedOptions(tp)...,
))
}
The xrayconfig.WithRecommendedOptions() includes:
- X-Ray propagator for trace context
- Lambda resource detector
- TracerProvider configuration
- Automatic flushing
AWS Lambda Resource Detector
The Lambda resource detector automatically populates these attributes:
| Attribute | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
cloud.provider | aws | Cloud provider name |
cloud.region | us-east-1 | AWS region |
faas.name | MyFunction | Lambda function name |
faas.version | $LATEST | Function version |
faas.instance | 2024/01/... | Execution instance ID |
faas.max_memory | 128 | Configured memory in MB |
To use the detector manually:
import (
"context"
"log"
lambdadetector "go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/detectors/aws/lambda"
sdktrace "go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/trace"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Detect Lambda resources
detector := lambdadetector.NewResourceDetector()
res, err := detector.Detect(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("failed to detect lambda resources: %v", err)
}
// Create TracerProvider with detected resources
tp := sdktrace.NewTracerProvider(
sdktrace.WithResource(res),
// ... other options
)
}
Environment Variables
Configure your Lambda function with these environment variables:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
UPTRACE_DSN | Uptrace DSN for sending telemetry |
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME | Service name for spans |
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES | Additional resource attributes |
OTEL_PROPAGATORS | Context propagators (tracecontext,baggage,xray) |
OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER | Sampling strategy |
Example AWS CLI configuration:
aws lambda update-function-configuration \
--function-name my-function \
--environment "Variables={UPTRACE_DSN=https://token@api.uptrace.dev/project_id,OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=my-lambda}"
Custom Event Handling
Extract trace context from custom event types (API Gateway, SQS, etc.):
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
"github.com/uptrace/uptrace-go/uptrace"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/attribute"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/propagation"
)
type APIGatewayEvent struct {
Headers map[string]string `json:"headers"`
Body string `json:"body"`
HTTPMethod string `json:"httpMethod"`
Path string `json:"path"`
}
func HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, event APIGatewayEvent) (string, error) {
return fmt.Sprintf("Processed %s %s", event.HTTPMethod, event.Path), nil
}
// Extract trace headers from API Gateway events
func apiGatewayEventToCarrier(eventJSON []byte) propagation.TextMapCarrier {
var event APIGatewayEvent
if err := json.Unmarshal(eventJSON, &event); err != nil {
return nil
}
return propagation.MapCarrier(event.Headers)
}
// Add custom attributes from event data
func apiGatewayAttributes(eventJSON []byte) []attribute.KeyValue {
var event APIGatewayEvent
if err := json.Unmarshal(eventJSON, &event); err != nil {
return nil
}
return []attribute.KeyValue{
attribute.String("http.method", event.HTTPMethod),
attribute.String("http.path", event.Path),
}
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
uptrace.ConfigureOpentelemetry(
uptrace.WithServiceName("my-api-gateway-lambda"),
)
defer uptrace.Shutdown(ctx)
tp := uptrace.TracerProvider()
lambda.Start(otellambda.InstrumentHandler(
HandleRequest,
otellambda.WithTracerProvider(tp),
otellambda.WithFlusher(tp),
otellambda.WithEventToCarrier(apiGatewayEventToCarrier),
otellambda.WithTraceAttributeFn(apiGatewayAttributes),
))
}
Cold Start Optimization
Minimize cold start impact:
- Initialize in init(): Configure OpenTelemetry once during cold start
- Keep dependencies minimal: Only import what you need
- Use environment variables: Avoid hardcoded configuration
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
"github.com/uptrace/uptrace-go/uptrace"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/otellambda"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel"
sdktrace "go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/trace"
)
var tracer = otel.Tracer("handler")
var tp *sdktrace.TracerProvider
// init runs once during cold start
func init() {
uptrace.ConfigureOpentelemetry(
uptrace.WithServiceName("my-lambda"),
)
tp = uptrace.TracerProvider()
}
func HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, event any) error {
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, "handle-request")
defer span.End()
// Your logic here
return nil
}
func main() {
lambda.Start(otellambda.InstrumentHandler(
HandleRequest,
otellambda.WithTracerProvider(tp),
otellambda.WithFlusher(tp),
))
}
OpenTelemetry Lambda Layer
As an alternative to manual instrumentation, you can use the OpenTelemetry Lambda layer with a Collector sidecar. This approach:
- Adds instrumentation via Lambda layers
- Runs a Collector as a Lambda extension
- Supports custom Collector configuration
See the Go example for details.
What is Uptrace?
Uptrace is an OpenTelemetry APM that supports distributed tracing, metrics, and logs. You can use it to monitor applications and troubleshoot issues.
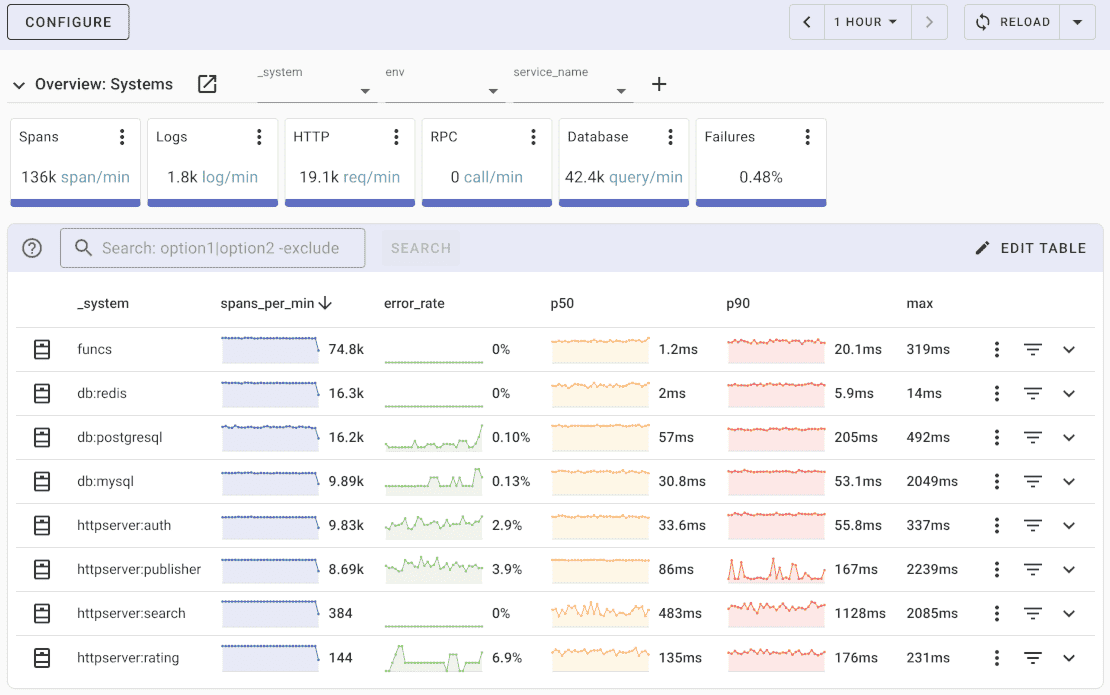
Uptrace comes with an intuitive query builder, rich dashboards, alerting rules with notifications, and integrations for most languages and frameworks.
Uptrace can process billions of spans and metrics on a single server and allows you to monitor your applications at 10x lower cost.
In just a few minutes, you can try Uptrace by visiting the cloud demo (no login required) or running it locally with Docker. The source code is available on GitHub.
What's next?
- OpenTelemetry Go guide - Complete Go instrumentation documentation
- OpenTelemetry Go Serverless - Serverless patterns for Vercel and GCP
- Node.js Lambda instrumentation - Alternative runtime option
- OpenTelemetry Go Tracing - Create custom spans and attributes
- OpenTelemetry Go Sampling - Reduce costs in high-volume functions