OpenTelemetry for Spring Boot: Guide with Examples
Monitoring distributed Spring Boot applications requires robust observability tools. This guide shows you how to implement OpenTelemetry for Spring Boot integration, covering automatic instrumentation, manual instrumentation examples, and production deployment strategies.
Choose Your Instrumentation Option
Spring Boot offers two main options for OpenTelemetry integration:
| Feature | Java Agent | Spring Boot Starter |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Complexity | Minimal (JAR + env vars) | Moderate (dependencies + config) |
| Code Changes | None required | Minimal (configuration) |
| Auto-Instrumentation | 150+ libraries | Common Spring libraries |
| Startup Overhead | 100-300ms | 50-100ms |
| Memory Footprint | +50-100MB | +20-40MB |
| Native Image Support | Not supported | Fully supported |
| Configuration | Env vars / system props | Spring application.yml |
| Best For | Quick POC, existing apps | Spring Boot 3, Native Image, Fine-grained control |
Recommendation:
- Use Java Agent for quickest setup with zero code changes and maximum auto-instrumentation coverage
- Use Spring Boot Starter for GraalVM Native Image, Spring-native configuration, or fine-grained control
For detailed Java Agent setup, see OpenTelemetry Java Agent for Spring Boot. For other Java instrumentation options, see the OpenTelemetry Java guide.
Components of Spring OpenTelemetry
Spring OpenTelemetry provides comprehensive observability through three pillars:
- Distributed Traces: Complete request flows across microservices with context propagation
- Application Metrics: Performance indicators, latency histograms, and business KPIs
- Structured Logs: Contextual events with automatic trace correlation
OpenTelemetry vs Micrometer in Spring
| Feature | OpenTelemetry | Micrometer |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Traces, Metrics, Logs | Primarily Metrics |
| Distributed Tracing | Full W3C standard support | Limited capabilities |
| Backend Support | Any OTLP-compatible system | Vendor-specific |
| Spring Integration | Auto + Manual instrumentation | Native Spring Boot |
| Semantic Conventions | Standardized attributes | Custom naming |
For a detailed comparison, see OpenTelemetry vs Micrometer.
Quick Start: For fastest setup without code changes, see the Java zero-code instrumentation guide.
Step-by-Step Spring Implementation
Option 1: Java Agent (Recommended)
Best for: Quick setup with zero code changes
The OpenTelemetry Java Agent provides automatic instrumentation for 150+ libraries including Spring MVC, WebFlux, JDBC, JPA, Kafka, and HTTP clients.
Step 1: Download the agent
curl -L -O https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-java-instrumentation/releases/latest/download/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
Step 2: Configure environment
export OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=spring-app
export OTEL_SERVICE_VERSION=1.0.0
export OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER=otlp
export OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER=otlp
export OTEL_LOGS_EXPORTER=otlp
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=https://api.uptrace.dev:4317
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS=uptrace-dsn=<your_uptrace_dsn>
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_COMPRESSION=gzip
Step 3: Run with instrumentation
java -javaagent:opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -jar your-spring-app.jar
For detailed configuration options and advanced usage, see OpenTelemetry Java Agent for Spring Boot.
Option 2: Spring Boot Starter
Best for: GraalVM Native Image, Spring-native configuration, and fine-grained control
The Spring Boot Starter integrates with Spring's auto-configuration system and supports Native Image compilation.
Dependencies:
Use the OpenTelemetry BOM (Bill of Materials) for consistent version management:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- Import OTel BOM BEFORE spring-boot-dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentelemetry.instrumentation</groupId>
<artifactId>opentelemetry-instrumentation-bom</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentelemetry.instrumentation</groupId>
<artifactId>opentelemetry-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Configuration (application.yml):
spring:
application:
name: spring-app
otel:
exporter:
otlp:
protocol: grpc
endpoint: https://api.uptrace.dev:4317
headers:
uptrace-dsn: <your_uptrace_dsn>
compression: gzip
resource:
attributes:
service.version: 1.0.0
deployment.environment: production
Configuration (application.properties):
spring.application.name=spring-app
otel.exporter.otlp.protocol=grpc
otel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=https://api.uptrace.dev:4317
otel.exporter.otlp.headers.uptrace-dsn=<your_uptrace_dsn>
otel.exporter.otlp.compression=gzip
otel.resource.attributes.service.version=1.0.0
otel.resource.attributes.deployment.environment=production
Out-of-the-Box Instrumentation
The Spring Boot Starter automatically instruments common Spring components:
| Feature | Configuration Property | Default |
|---|---|---|
| JDBC | otel.instrumentation.jdbc.enabled | true |
| Spring Web | otel.instrumentation.spring-web.enabled | true |
| Spring WebMVC | otel.instrumentation.spring-webmvc.enabled | true |
| Spring WebFlux | otel.instrumentation.spring-webflux.enabled | true |
| R2DBC (Reactive) | otel.instrumentation.r2dbc.enabled | true |
| Kafka | otel.instrumentation.kafka.enabled | true |
| MongoDB | otel.instrumentation.mongo.enabled | true |
| Logback Appender | otel.instrumentation.logback-appender.enabled | true |
| Logback MDC | otel.instrumentation.logback-mdc.enabled | true |
| Micrometer | otel.instrumentation.micrometer.enabled | false |
Service Name Configuration
The service name is determined in this order of precedence:
otel.service.nameproperty orOTEL_SERVICE_NAMEenv varservice.nameinotel.resource.attributesspring.application.namepropertybuild-info.properties(generated by Spring Boot Maven/Gradle plugin)- Default:
unknown_service:java
To automatically use your project name, add the build-info goal:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>build-info</goal>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
SDK Configuration Options
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
otel.exporter.otlp.endpoint | OTLP endpoint URL | http://localhost:4318 |
otel.exporter.otlp.protocol | Protocol (grpc or http/protobuf) | http/protobuf |
otel.exporter.otlp.headers.* | Custom headers for authentication | - |
otel.exporter.otlp.compression | Compression (gzip or none) | none |
otel.traces.exporter | Traces exporter (otlp, logging, none) | otlp |
otel.metrics.exporter | Metrics exporter | otlp |
otel.logs.exporter | Logs exporter | otlp |
otel.propagators | Context propagators | tracecontext,baggage |
otel.sdk.disabled | Disable OpenTelemetry (for testing) | false |
GraalVM Native Image Support
The Spring Boot Starter fully supports GraalVM Native Image compilation, making it the preferred choice for native applications:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.graalvm.buildtools</groupId>
<artifactId>native-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Build and run the native image:
# Maven
./mvnw -Pnative native:compile
./target/your-app
# Gradle
./gradlew nativeCompile
./build/native/nativeCompile/your-app
Native images start in milliseconds and have significantly lower memory footprint compared to JVM-based deployments.
Spring WebFlux (Reactive) Support
Both the Java Agent and Spring Boot Starter provide full support for Spring WebFlux reactive applications.
Reactive Controller Example
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/orders")
public class ReactiveOrderController {
private final OrderService orderService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Mono<Order> getOrder(@PathVariable String id) {
// Automatically instrumented - spans propagate through reactive chain
return orderService.findById(id)
.doOnSuccess(order -> log.info("Found order: {}", order.getId()));
}
@GetMapping("/stream")
public Flux<Order> streamOrders() {
// Streaming endpoint also instrumented
return orderService.streamAllOrders();
}
}
WebClient Instrumentation
Outbound HTTP calls with WebClient are automatically traced:
@Service
public class PaymentClient {
private final WebClient webClient;
public PaymentClient(WebClient.Builder builder) {
this.webClient = builder
.baseUrl("https://payment-service")
.build();
}
public Mono<PaymentResult> processPayment(Payment payment) {
// Trace context automatically propagated to downstream service
return webClient.post()
.uri("/api/payments")
.bodyValue(payment)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(PaymentResult.class);
}
}
Annotation-Based Instrumentation
The Spring Boot Starter supports @WithSpan and @SpanAttribute annotations for declarative instrumentation without manual span management.
Setup
Add the Spring AOP dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
@WithSpan Annotation
Automatically wrap methods in spans:
import io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.annotations.WithSpan;
import io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.annotations.SpanAttribute;
import io.opentelemetry.api.trace.SpanKind;
@Service
public class OrderService {
@WithSpan
public Order processOrder(String orderId) {
// Creates span named "OrderService.processOrder"
return doProcess(orderId);
}
@WithSpan("custom-operation-name")
public void customNamedOperation() {
// Creates span with custom name
}
@WithSpan(kind = SpanKind.CLIENT)
public ExternalResult callExternalService() {
// Creates CLIENT span for external calls
}
@WithSpan
public Order findOrder(
@SpanAttribute("order.id") String orderId,
@SpanAttribute("customer.id") String customerId) {
// Captures method parameters as span attributes
return repository.find(orderId);
}
}
Important limitations:
- Annotations only work on Spring-proxied beans
- Internal method calls within the same class are not instrumented
- Disable with:
otel.instrumentation.annotations.enabled=false
Programmatic Configuration
For advanced customization, use AutoConfigurationCustomizerProvider beans:
import io.opentelemetry.sdk.autoconfigure.spi.AutoConfigurationCustomizerProvider;
import io.opentelemetry.semconv.UrlAttributes;
import io.opentelemetry.contrib.sampler.RuleBasedRoutingSampler;
import io.opentelemetry.api.trace.SpanKind;
@Configuration
public class OtelConfiguration {
@Bean
public AutoConfigurationCustomizerProvider otelCustomizer() {
return p -> p.addSamplerCustomizer((sampler, config) ->
RuleBasedRoutingSampler.builder(SpanKind.SERVER, sampler)
.drop(UrlAttributes.URL_PATH, "^/actuator")
.drop(UrlAttributes.URL_PATH, "^/health")
.build()
);
}
}
This example filters out health check endpoints from tracing.
Logging Integration
OpenTelemetry provides automatic log correlation with traces. The Spring Boot Starter automatically configures Logback integration without requiring manual logback.xml changes.
Automatic Configuration (Spring Boot Starter)
When using the Spring Boot Starter, logging instrumentation is enabled by default:
- Logback Appender: Exports logs via OTLP (
otel.instrumentation.logback-appender.enabled=true) - MDC Injection: Adds trace/span IDs to MDC (
otel.instrumentation.logback-mdc.enabled=true)
Configure experimental features via application properties:
# Capture thread name and ID
otel.instrumentation.logback-appender.experimental-log-attributes=true
# Capture source code location (may add overhead)
otel.instrumentation.logback-appender.experimental.capture-code-attributes=true
# Capture all MDC attributes
otel.instrumentation.logback-appender.experimental.capture-mdc-attributes=*
Custom Logback Configuration
For more control, configure manually in logback-spring.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} trace_id=%X{trace_id} span_id=%X{span_id} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<appender name="OpenTelemetry"
class="io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.logback.appender.v1_0.OpenTelemetryAppender">
<captureExperimentalAttributes>true</captureExperimentalAttributes>
<captureCodeAttributes>true</captureCodeAttributes>
<captureMdcAttributes>*</captureMdcAttributes>
</appender>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
<appender-ref ref="OpenTelemetry"/>
</root>
</configuration>
For complete configuration options, see the OpenTelemetry Logback guide.
Log4j2 Configuration
For Log4j2, see the OpenTelemetry Log4j guide.
Custom Instrumentation for Business Telemetry
For comprehensive manual instrumentation patterns with complete working examples, see OpenTelemetry Java Manual Instrumentation.
Custom Trace Implementation
This example shows how to create custom spans that capture business-specific context and operations:
@Service
public class OrderProcessingService {
private final Tracer tracer;
public OrderProcessingService(OpenTelemetry openTelemetry) {
this.tracer = openTelemetry.getTracer("com.example.orders", "1.0.0");
}
public OrderResult processOrder(OrderRequest request) {
Span orderSpan = tracer.spanBuilder("process-order")
.setAttribute("order.id", request.getOrderId())
.setAttribute("customer.id", request.getCustomerId())
.setAttribute("order.amount", request.getTotalAmount())
.startSpan();
try (Scope scope = orderSpan.makeCurrent()) {
// Business logic with automatic context propagation
validateOrder(request);
orderSpan.addEvent("order.validated");
PaymentResult payment = processPayment(request);
orderSpan.setAttribute("payment.status", payment.getStatus());
OrderResult result = finalizeOrder(request);
orderSpan.setStatus(StatusCode.OK);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
orderSpan.setStatus(StatusCode.ERROR, e.getMessage());
orderSpan.recordException(e);
throw e;
} finally {
orderSpan.end();
}
}
}
Business Metrics Collection
Use this pattern to capture custom business metrics that provide insights into your application's performance and user behavior:
@Component
public class BusinessMetricsCollector {
private final LongCounter orderCounter;
private final DoubleHistogram orderValueHistogram;
public BusinessMetricsCollector(OpenTelemetry openTelemetry) {
Meter meter = openTelemetry.getMeter("com.example.business", "1.0.0");
orderCounter = meter.counterBuilder("orders.processed.total")
.setDescription("Total orders processed")
.build();
orderValueHistogram = meter.histogramBuilder("order.value")
.setDescription("Order value distribution")
.setUnit("USD")
.build();
}
public void recordOrder(String type, String status, double value) {
orderCounter.add(1, Attributes.of(
AttributeKey.stringKey("order.type"), type,
AttributeKey.stringKey("order.status"), status
));
orderValueHistogram.record(value, Attributes.of(
AttributeKey.stringKey("order.type"), type
));
}
}
Enhanced Controller Instrumentation
Here's how to enrich your REST controllers with additional telemetry context and business metrics:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/orders")
public class OrderController {
private final OrderProcessingService orderService;
private final BusinessMetricsCollector metricsCollector;
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<OrderResponse> createOrder(@RequestBody OrderRequest request) {
// Current span enrichment
Span currentSpan = Span.current();
currentSpan.setAttribute("order.items.count", request.getItems().size());
currentSpan.setAttribute("customer.region", request.getCustomerRegion());
try {
OrderResult result = orderService.processOrder(request);
// Record business metrics
metricsCollector.recordOrder(
request.getOrderType(),
result.getStatus(),
request.getTotalAmount()
);
currentSpan.setStatus(StatusCode.OK);
return ResponseEntity.ok(new OrderResponse(result.getOrderId()));
} catch (OrderValidationException e) {
currentSpan.setStatus(StatusCode.ERROR, "Validation failed");
return ResponseEntity.badRequest()
.body(new ErrorResponse("VALIDATION_ERROR", e.getMessage()));
}
}
}
OpenTelemetry Collector Setup
The OpenTelemetry Collector acts as a vendor-agnostic proxy between your Spring Boot applications and your observability backend, providing buffering, batching, and data transformation.
Basic Configuration
# otel-collector-config.yaml
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
processors:
batch:
timeout: 5s
send_batch_size: 1000
memory_limiter:
check_interval: 1s
limit_mib: 1000
spike_limit_mib: 200
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: https://api.uptrace.dev:4317
headers:
uptrace-dsn: ${UPTRACE_DSN}
compression: gzip
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [memory_limiter, batch]
exporters: [otlp]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [memory_limiter, batch]
exporters: [otlp]
logs:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [memory_limiter, batch]
exporters: [otlp]
Kubernetes Deployment
Deploy your Spring Boot application with the collector in Kubernetes:
# deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: spring-app
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: spring-app
image: your-spring-app:latest
env:
- name: OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
value: spring-app
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: http://otel-collector:4317
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL
value: grpc
- name: OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER
value: parentbased_traceidratio
- name: OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER_ARG
value: "0.1"
Docker Compose Deployment
# docker-compose.yml
services:
spring-app:
image: your-spring-app:latest
environment:
- OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=spring-app
- OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc
- OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=http://otel-collector:4317
- OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER=parentbased_traceidratio
- OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER_ARG=0.1
depends_on:
- otel-collector
otel-collector:
image: otel/opentelemetry-collector-contrib:latest
command: ["--config=/etc/otel-collector-config.yaml"]
environment:
- UPTRACE_DSN=${UPTRACE_DSN}
volumes:
- ./otel-collector-config.yaml:/etc/otel-collector-config.yaml
ports:
- "4317:4317"
- "4318:4318"
Troubleshooting
No Telemetry Data
Symptoms: Application runs but no traces appear in backend
Diagnosis:
# Enable debug logging for Java Agent
export OTEL_JAVAAGENT_DEBUG=true
# For Spring Boot Starter, add to application.properties
logging.level.io.opentelemetry=DEBUG
# Check connectivity to collector
curl -v http://your-collector:4318/v1/traces
Common causes and solutions:
- Wrong endpoint URL: Ensure the endpoint matches your collector configuration
- Protocol mismatch: Default changed to
http/protobufin recent versions - Missing headers: Check authentication headers are set correctly
otel:
exporter:
otlp:
endpoint: http://collector:4318
protocol: http/protobuf
Broken Trace Propagation
Symptoms: Disconnected spans across services, missing parent-child relationships
Diagnosis:
@GetMapping("/debug/trace")
public Map<String, String> debugTrace(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>();
headers.put("traceparent", request.getHeader("traceparent"));
headers.put("current-trace-id", Span.current().getSpanContext().getTraceId());
headers.put("current-span-id", Span.current().getSpanContext().getSpanId());
return headers;
}
Common causes:
- Missing propagator configuration: Ensure W3C Trace Context is enabled
- HTTP client not instrumented: Check RestTemplate/WebClient are auto-instrumented
- Async operations: Context may not propagate across thread boundaries
Solution for custom propagation:
@Bean
public TextMapPropagator textMapPropagator() {
return TextMapPropagator.composite(
W3CTraceContextPropagator.getInstance(),
W3CBaggagePropagator.getInstance()
);
}
High Memory Usage
Symptoms: Increasing heap usage, frequent GC, OutOfMemoryError
Solutions:
# Reduce batch queue size
export OTEL_BSP_MAX_QUEUE_SIZE=1024
export OTEL_BSP_MAX_EXPORT_BATCH_SIZE=256
export OTEL_BSP_SCHEDULE_DELAY=2000
# Implement sampling to reduce trace volume
export OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER=parentbased_traceidratio
export OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER_ARG=0.1
# Disable unused instrumentations
export OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_SPRING_SCHEDULING_ENABLED=false
Slow Application Startup
Symptoms: Application takes longer to start with Java Agent
Solutions:
- Use Spring Boot Starter instead of Java Agent for faster startup
- Disable unused instrumentations:
export OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_COMMON_DEFAULT_ENABLED=false
export OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_SPRING_WEBMVC_ENABLED=true
export OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_JDBC_ENABLED=true
- For Native Image, use Spring Boot Starter (Java Agent not supported)
Connection Timeouts
Symptoms: "Failed to export spans" errors in logs
Solutions:
# Increase timeout
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_TIMEOUT=30000
# Enable compression
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_COMPRESSION=gzip
# Use async exporter
export OTEL_BSP_SCHEDULE_DELAY=5000
Performance and Resource Impact
Performance Impact Analysis
| Component | Overhead | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Usage | 3-8% | Optimize sampling rates |
| Memory | 10-15% | Configure buffer limits |
| Network | 5-10KB/request | Enable compression |
| Latency | 1-5ms/request | Use async exporters |
Production Optimization
These environment variables help optimize OpenTelemetry performance for high-traffic production environments:
# JVM optimization
export JAVA_OPTS="-XX:+UseG1GC -Xms2g -Xmx4g"
# OpenTelemetry performance tuning
export OTEL_BSP_SCHEDULE_DELAY=5000
export OTEL_BSP_MAX_EXPORT_BATCH_SIZE=512
export OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER_ARG=0.1
# Disable unnecessary instrumentation
export OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_LOGBACK_APPENDER_ENABLED=false
Best Practices
Environment-Specific Configurations
Development:
otel:
traces:
sampler: parentbased_always_on # Full sampling
exporter:
otlp:
protocol: grpc
endpoint: http://localhost:4317
Production:
otel:
traces:
sampler: parentbased_traceidratio
sampler.arg: 0.1 # Controlled sampling
exporter:
otlp:
protocol: grpc
endpoint: https://prod-collector:4317
compression: gzip
Monitoring Strategy
- Start Simple: Begin with Java Agent for immediate results
- Add Context: Implement custom instrumentation for business insights
- Optimize Gradually: Fine-tune sampling and performance settings
- Monitor Impact: Track OpenTelemetry's resource usage
- Scale Appropriately: Adjust configuration based on traffic patterns
What is Uptrace?
Uptrace is an OpenTelemetry APM that supports distributed tracing, metrics, and logs. You can use it to monitor applications and troubleshoot issues.
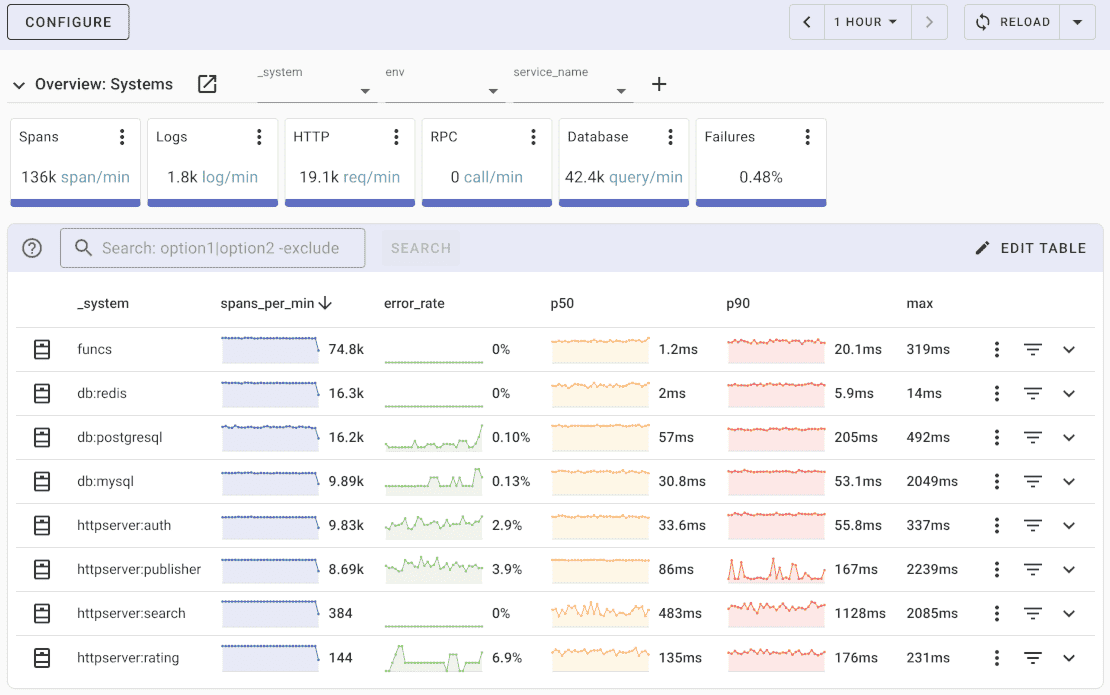
Uptrace comes with an intuitive query builder, rich dashboards, alerting rules with notifications, and integrations for most languages and frameworks.
Uptrace can process billions of spans and metrics on a single server and allows you to monitor your applications at 10x lower cost.
In just a few minutes, you can try Uptrace by visiting the cloud demo (no login required) or running it locally with Docker. The source code is available on GitHub.
What's Next?
OpenTelemetry Spring Boot integration provides comprehensive observability for your Java applications. Here are recommended next steps:
By Use Case
| I want to... | Read this |
|---|---|
| Use zero-code instrumentation | Java Agent for Spring Boot |
| Add custom spans and metrics | Manual Instrumentation |
| Configure log correlation | Logback integration or Log4j integration |
| Monitor Tomcat containers | Tomcat instrumentation |
| Compare with Micrometer | OpenTelemetry vs Micrometer |
| Understand sampling | Sampling strategies |
| Configure context propagation | Context propagation |
Related Guides
- OpenTelemetry Java guide - Core Java SDK documentation
- OpenTelemetry Quarkus - Quarkus instrumentation with native image support
- Spring Boot Microservices Monitoring - Monitoring patterns for microservices
- OpenTelemetry Collector - Collector configuration and deployment