OpenTelemetry Slog [otelslog]: Golang Bridge Setup & Examples
OpenTelemetry Slog (otelslog) is a bridge handler for Golang's standard structured logging library. The handler intercepts log messages and injects OpenTelemetry trace context, including trace and span IDs that correlate logs with specific requests in distributed systems. This guide covers otelslog setup, slog.SetDefault configuration, and Golang OTel logging best practices.
Quick Setup
Install the otelslog bridge and configure slog with OpenTelemetry:
go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog
import "go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog"
slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("your-service-name"))
Now all slog calls automatically include OpenTelemetry trace context.
What is OpenTelemetry?
OpenTelemetry is an open-source observability framework that aims to standardize and simplify the collection, processing, and export of telemetry data from applications and systems.
OpenTelemetry supports multiple programming languages and platforms, making it suitable for a wide range of applications and environments.
OpenTelemetry enables developers to instrument their code and collect telemetry data, which can then be exported to various OpenTelemetry backends or observability platforms for analysis and visualization.
What is otelslog?
otelslog is the official OpenTelemetry bridge for Go's slog package, provided by go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog. It implements the slog.Handler interface to automatically inject trace context (trace ID, span ID) into log records, enabling correlation between logs and distributed traces.
Installation
Install the otelslog bridge package:
go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog
Basic Configuration with slog.SetDefault
The slog.SetDefault() function sets the global default logger used by top-level logging functions like slog.Info(), slog.Error(), etc. Configure it with otelslog to enable automatic trace context injection:
import (
"log/slog"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog"
)
func main() {
// Set otelslog as the default global logger
slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("app_or_package_name"))
// All slog calls now include OTel trace context
slog.Info("Application started")
}
Resources:
Complete Golang OTel Logging Example
Here's a full example showing otelslog integration with OpenTelemetry tracing:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log/slog"
"github.com/uptrace/uptrace-go/uptrace"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/trace"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Initialize OpenTelemetry
uptrace.ConfigureOpentelemetry(
uptrace.WithServiceName("slog-example"),
)
defer uptrace.Shutdown(ctx)
// Configure slog with OTel handler
slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("slog-example"))
// Create tracer for instrumenting operations
tracer := otel.Tracer("slog-example")
// Start a traced operation
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, "process-request")
defer span.End()
// Structured logging with trace context
slog.InfoContext(ctx, "Processing request",
"user_id", "12345",
"action", "login")
// Log errors with full context
slog.ErrorContext(ctx, "Authentication failed",
"locale", "en_US",
"reason", "invalid_credentials")
// View trace in Uptrace
fmt.Println("Trace URL:", uptrace.TraceURL(trace.SpanFromContext(ctx)))
}
Key Benefits:
- Logs automatically include trace_id and span_id from context
- Correlate logs with distributed traces across microservices
- Compatible with all OpenTelemetry-compliant backends
- No vendor lock-in - works with Uptrace, Jaeger, Datadog, etc.
Golang OTel Logging Best Practices
Use Context-Aware Logging
Always use slog.InfoContext() instead of slog.Info() to include trace context:
// Good: Includes trace context
slog.InfoContext(ctx, "User logged in", "user_id", userId)
// Bad: Missing trace context
slog.Info("User logged in", "user_id", userId)
Structured Fields for Filtering
Use key-value pairs for structured logging to enable powerful filtering:
slog.InfoContext(ctx, "Database query executed",
"query_type", "SELECT",
"table", "users",
"duration_ms", 45,
"rows_affected", 1,
)
Log Levels Strategy
Debug: Detailed information for debugging (disabled in production)Info: General operational eventsWarn: Potentially harmful situationsError: Errors that should be investigated
// Development
slog.SetLogLoggerLevel(slog.LevelDebug)
// Production
slog.SetLogLoggerLevel(slog.LevelInfo)
Log vs Slog Comparison
Golang introduced log/slog in Go 1.21 as the new standard structured logging library. Here's how it compares to the old log package:
| Feature | log (old) | slog (new) | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured logging | No | Yes | Machine-readable logs |
| Log levels | No | Yes (Debug, Info, Warn, Error) | Better filtering |
| Context support | No | Yes | Trace correlation |
| Performance | Slower | Faster | Lower overhead |
| Handlers | No | Yes | Flexible output formats |
| Standard library | Since Go 1.0 | Since Go 1.21 | Built-in |
Migration from log to slog:
// Old: log package
import "log"
log.Printf("User %s logged in", userId)
// New: slog package
import "log/slog"
slog.Info("User logged in", "user_id", userId)
// With OTel: otelslog
import "go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog"
slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("my-app"))
slog.InfoContext(ctx, "User logged in", "user_id", userId)
OpenTelemetry Slog adheres to the OpenTelemetry standards, ensuring compatibility with various tracing and monitoring tools that support OpenTelemetry. This flexibility prevents vendor lock-in and simplifies integration with your existing monitoring infrastructure.
What is Uptrace?
Uptrace is a OpenTelemetry APM that supports distributed tracing, metrics, and logs. You can use it to monitor applications and troubleshoot issues.
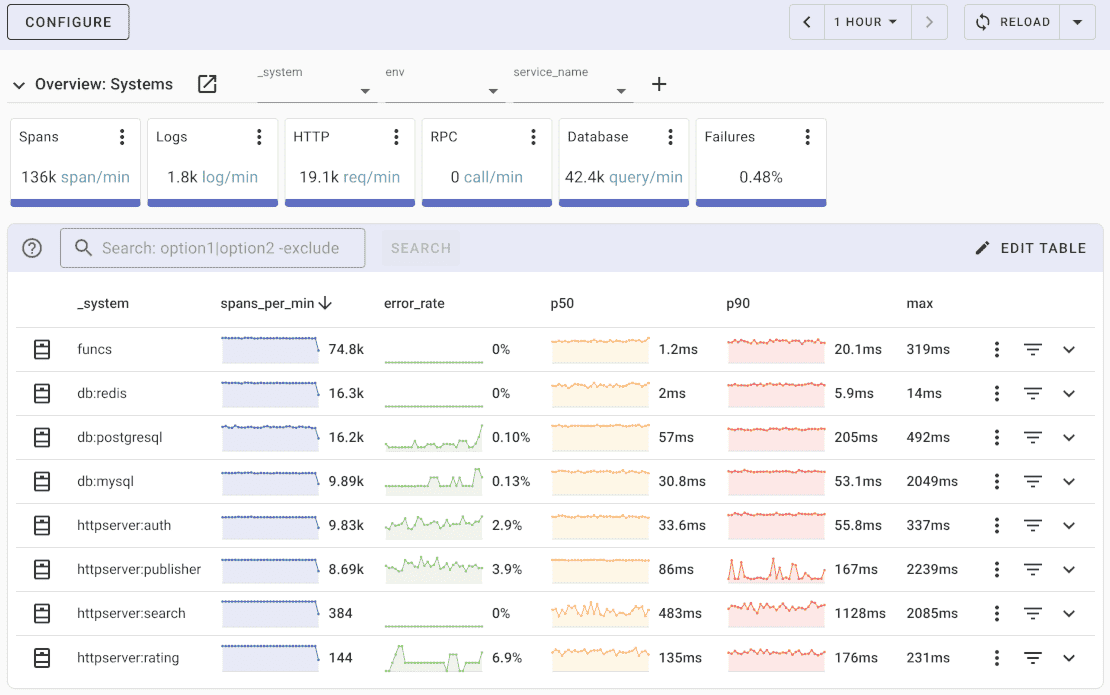
Uptrace comes with an intuitive query builder, rich dashboards, alerting rules with notifications, and integrations for most languages and frameworks.
Uptrace can process billions of spans and metrics on a single server and allows you to monitor your applications at 10x lower cost.
In just a few minutes, you can try Uptrace by visiting the cloud demo (no login required) or running it locally with Docker. The source code is available on GitHub.
FAQ
What is otelslog? otelslog is the official OpenTelemetry bridge for Go's slog package, available at go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog. It implements the slog.Handler interface to automatically inject trace context (trace ID, span ID) into log records, enabling correlation between logs and distributed traces in OpenTelemetry-based observability systems.
How to use slog with OpenTelemetry? Install go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog, then configure with slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("service-name")). Use slog.InfoContext(ctx, "message", "key", value) instead of slog.Info() to automatically include trace context from the provided context. This correlates logs with traces in your observability backend.
What is slog.SetDefault? slog.SetDefault() sets the global default logger used by package-level functions like slog.Info(), slog.Error(), etc. When called with slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("app")), all subsequent slog calls automatically use the otelslog handler, injecting OpenTelemetry trace context into every log entry without requiring explicit handler configuration at each call site.
Golang log vs slog - which to use? Use log/slog (introduced in Go 1.21) over the old log package. Slog provides structured logging with key-value pairs, log levels (Debug, Info, Warn, Error), better performance, and context support for trace correlation. The old log package lacks these features and should only be used in legacy code. Migrate to slog for modern Golang applications.
How to configure golang otel logging? Configure Golang OTel logging by: 1) Install otelslog bridge (go get go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/bridges/otelslog), 2) Initialize OpenTelemetry SDK, 3) Set default logger (slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("service-name"))), 4) Use context-aware logging (slog.InfoContext(ctx, "msg", "key", val)). This automatically includes trace_id and span_id in all log entries for correlation with distributed traces.
Does otelslog work with existing slog handlers? Yes, otelslog can be combined with other slog handlers using slog.Handler composition. For example, you can wrap otelslog with a JSON handler for structured output: handler := slog.NewJSONHandler(os.Stdout, nil) then create a multi-handler setup. However, most users set otelslog as the default handler since it automatically formats logs with trace context.
How to integrate slog with Uptrace? After configuring Uptrace with uptrace.ConfigureOpentelemetry(), set slog default to otelslog: slog.SetDefault(otelslog.NewLogger("your-service")). Use slog.InfoContext(ctx, "message", "key", value) in traced operations. Logs appear in Uptrace correlated with traces via trace_id, enabling seamless navigation from traces to related logs and vice versa for complete observability.
What is the performance impact of otelslog? otelslog adds minimal overhead (<1% in most applications) since it only extracts trace context from the provided context and appends it to log records. The slog package itself is highly optimized with zero-allocation structured logging. For high-throughput applications, use appropriate log levels (avoid Debug in production) and consider sampling strategies for trace collection.
What's next?
OpenTelemetry Slog is a valuable tool for improving the observability of Golang applications that use Slog for logging. By correlating logs with OpenTelemetry trace context, you can gain a deeper understanding of your application's behavior and more effectively diagnose problems and optimize performance. For comprehensive Go instrumentation, see the OpenTelemetry Go guide and explore top APM tools.