Log Analyzer and Log Analysis Tools for 2025
Log analysis tools parse, search, and visualize log data from servers, applications, and networks. These tools help identify security threats, troubleshoot errors, and monitor system performance by analyzing log files in real-time or historically. Open source options (ELK Stack, Graylog) and commercial platforms (Splunk, Datadog) offer different trade-offs in cost, features, and ease of use.
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Type | License | Best For | Search | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Splunk | Commercial | Proprietary | Enterprise security | SPL | ~$150/GB |
| ELK Stack | Open Source | Apache 2.0/Elastic | DevOps teams | Elasticsearch | Free/Paid |
| Datadog | Commercial | SaaS | Unified observability | Query builder | ~$0.10/GB+ |
| Graylog | Open Source | SSPL | Stream processing | Lucene | Free/Paid |
| Sumo Logic | Commercial | SaaS | Cloud security | CQL | ~$0.20/GB |
| New Relic | Commercial | SaaS | APM integration | NRQL | Free tier + |
| Loki | Open Source | AGPL | Cost-efficient | LogQL | Free |
| Uptrace | Open Source | AGPL/Commercial | Unified logs+traces | SQL | Free/Paid |
Log Analysis vs Log Management
Log Analysis focuses on searching, parsing, and visualizing logs to find patterns, errors, and security threats. Analysis tools (Splunk, ELK) provide query languages, dashboards, and anomaly detection.
Log Management handles collection, storage, and retention of logs from multiple sources. Management tools (Fluentd, Vector) focus on log shipping and centralization.
Most tools combine both - this guide focuses on analysis capabilities (search, visualization, alerting).
What is Log Analysis?
Log analysis is the process of examining, parsing, and interpreting log files generated by systems, applications, and network devices to extract meaningful insights about performance, security, and operational status. Unlike basic monitoring tools that track predefined metrics, log analysis tools process unstructured text data to identify patterns, anomalies, and security threats in real-time.
Top Log Analysis Tools in 2025
Uptrace
Market Position: Emerging unified observability platform with integrated log analysis
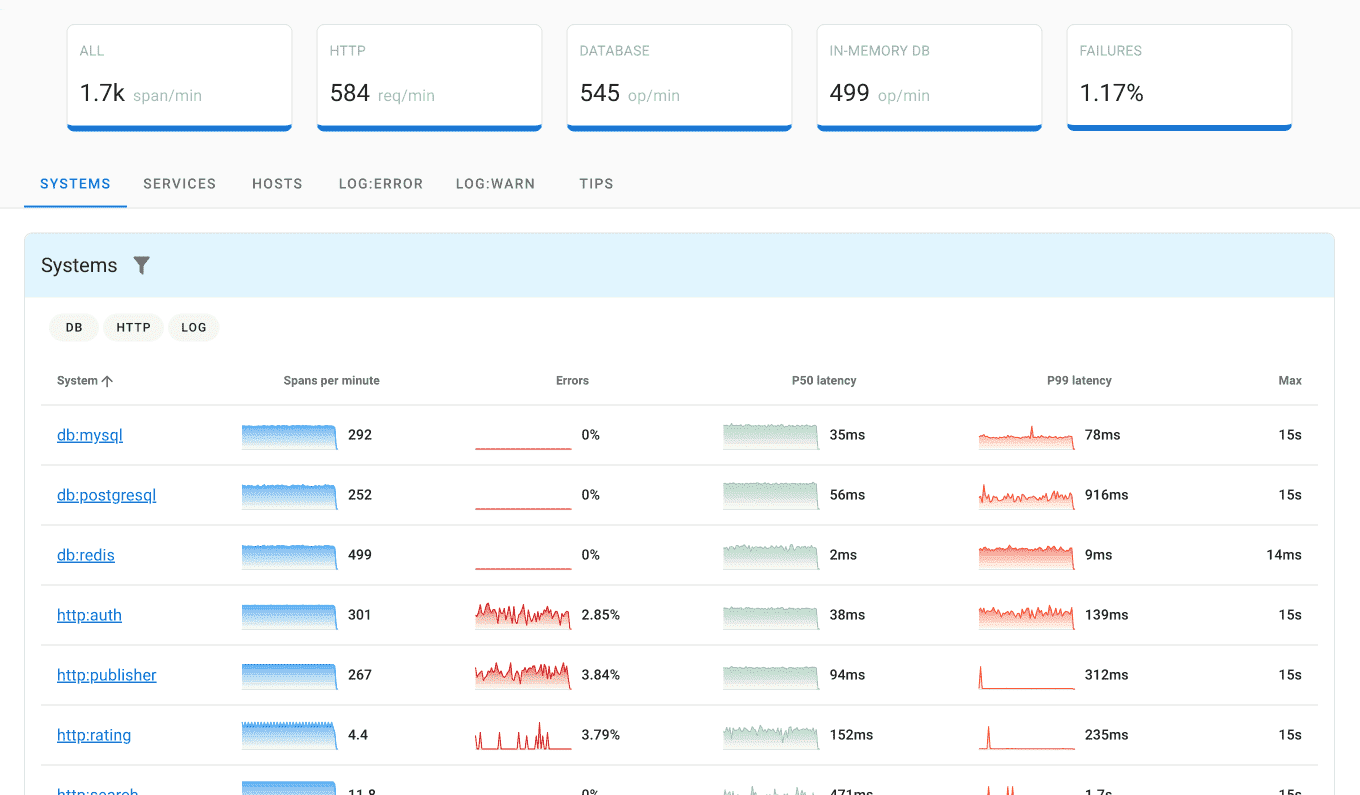
Why Choose Uptrace: Combines log analysis with distributed tracing and metrics in a single platform, offering enterprise features at startup-friendly pricing with OpenTelemetry-native architecture.
Key Features:
- Unified Observability: Logs, metrics, and traces in single platform
- OpenTelemetry Native: Built-in support for modern observability standards
- Advanced Correlation: Intelligent correlation between different data types
- Cost-Effective: Transparent pricing without per-user or per-host fees
Best For: Teams wanting unified observability with cost-effective log analysis
Pros: Unified platform, excellent value, modern architecture
Cons: Newer in market, smaller ecosystem than established vendors
Splunk
Type: Commercial SIEM platform
License: Proprietary
Search: SPL (Search Processing Language)
Best for: Enterprise security and compliance
Splunk dominates enterprise log analysis with 47.51% SIEM market share and 17,915+ customers. SPL query language offers powerful search capabilities for security investigations, while machine learning detects anomalies across petabyte-scale log volumes.
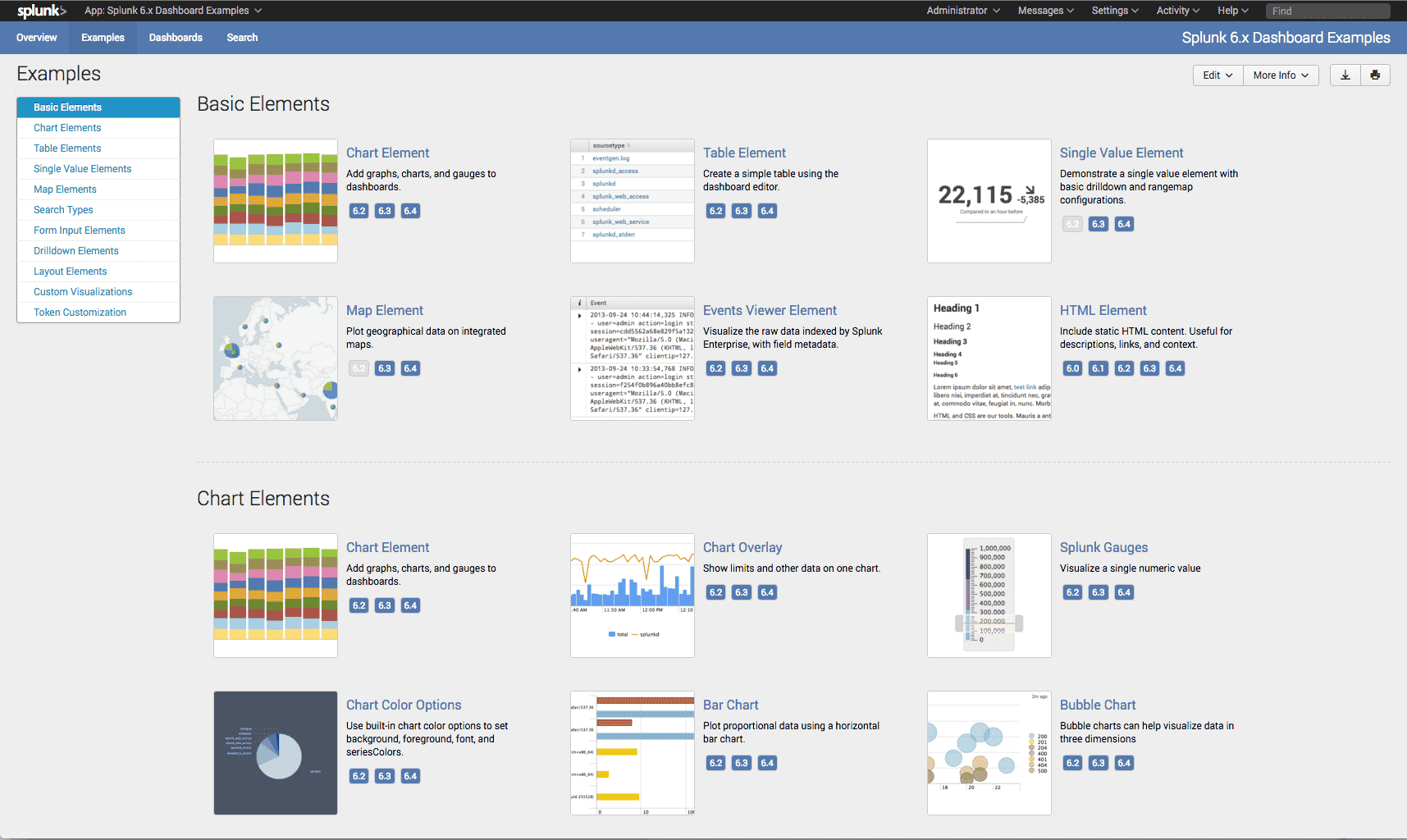
Key Features:
- SPL query language for complex log searches
- Machine learning anomaly detection
- SIEM and threat intelligence integration
- Petabyte-scale distributed architecture
Pros: Industry-leading features, strong security focus, enterprise support
Cons: Expensive at scale (~$150/GB), steep learning curve, complex setup
Pricing: ~$150/GB ingested (volume-based)
ELK Stack
Market Position: Leading open-source standard with 5,000+ enterprise deployments
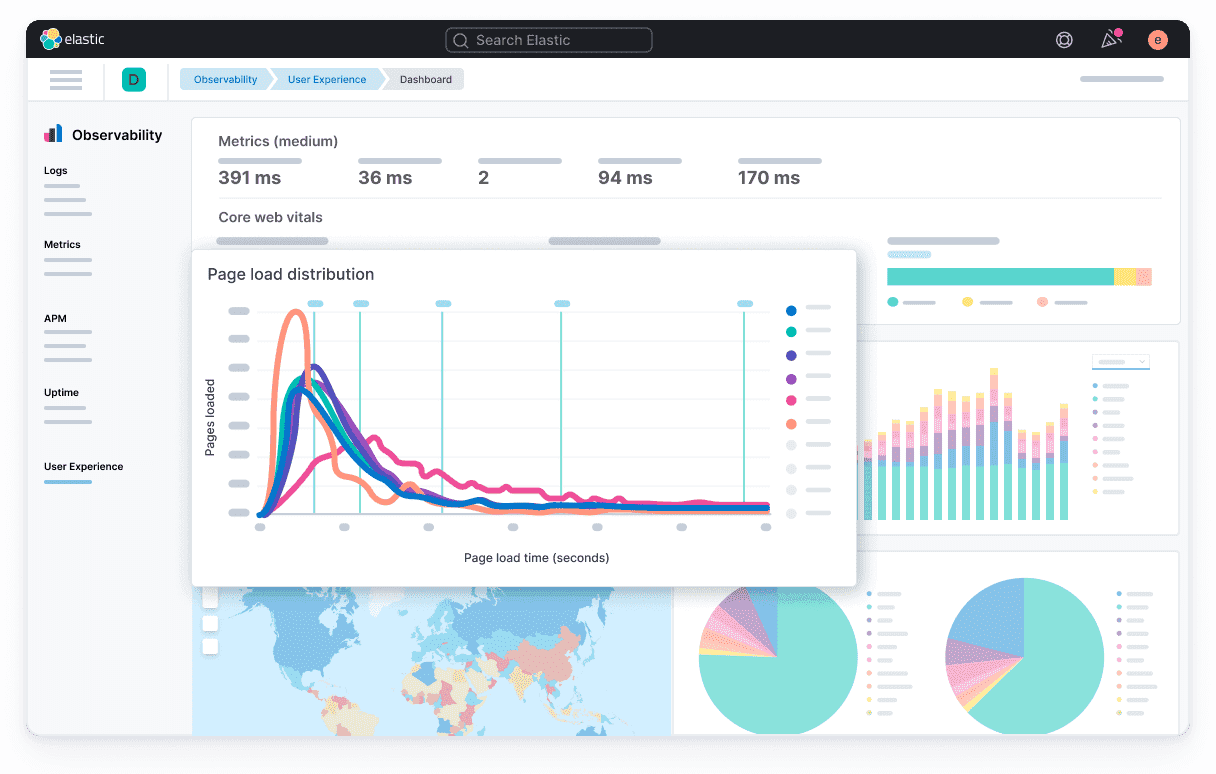
Why Choose ELK Stack: The most popular open-source log analysis solution, offering enterprise-grade capabilities without licensing costs. Ideal for organizations with technical expertise wanting full control over their log analysis infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Elasticsearch: Distributed search engine for fast log queries
- Logstash: Flexible data processing pipeline with 200+ plugins
- Kibana: Rich visualization and dashboard capabilities
- Beats: Lightweight data shippers for log collection
Best For: Organizations with DevOps expertise wanting customizable, cost-effective solutions
Pros: No licensing costs, highly customizable, strong community support
Cons: Requires technical expertise, resource-intensive, complex scaling
Datadog Logs
Type: Commercial observability platform
License: Proprietary SaaS
Search: Query builder
Best for: Unified observability
Datadog integrates log analysis with infrastructure monitoring and APM tools, serving 30,500+ customers. Excellent correlation between logs, metrics, and traces in unified platform.
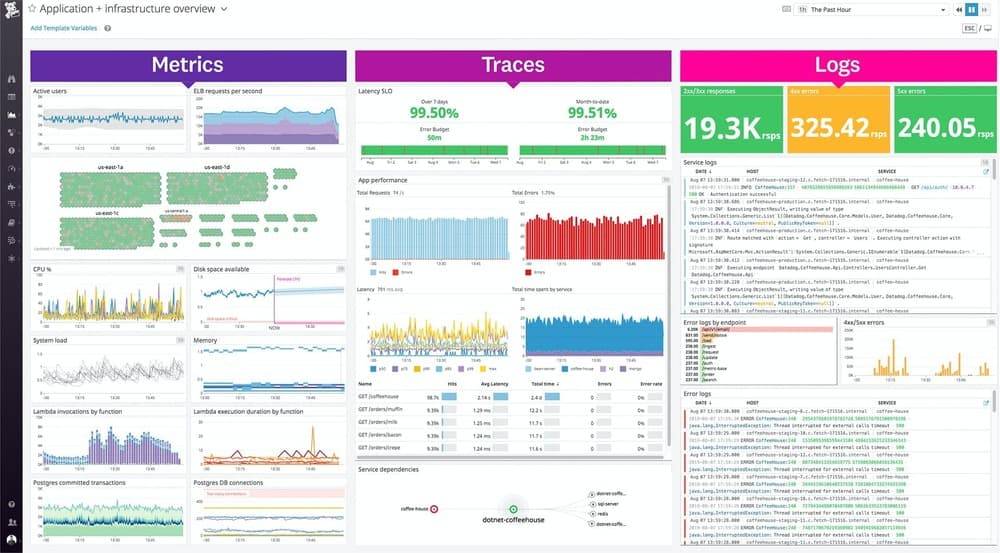
Key Features:
- Live Tail for real-time log streaming
- Automatic log-to-trace-to-metric correlation
- AI-powered pattern detection and clustering
- Unified logs, metrics, and traces platform
Pros: Excellent integration, user-friendly, powerful correlation
Cons: Expensive at scale, vendor lock-in concerns
Pricing: ~$0.10/GB ingestion + $1.70 per million events for indexing
Graylog
Market Position: Popular open-source enterprise solution with flexible commercial options
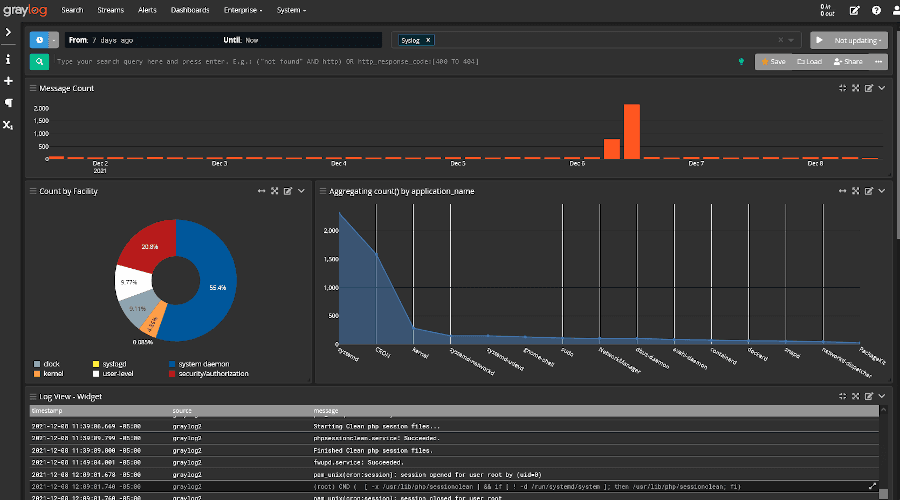
Why Choose Graylog: Combines open-source flexibility with enterprise features, offering powerful stream processing and real-time analysis. Excellent balance between cost-effectiveness and advanced capabilities.
Key Features:
- Stream Processing: Real-time log processing and enrichment
- Dynamic Pipelines: Custom log transformation and routing rules
- Centralized Management: Unified configuration across distributed collectors
- Alert Framework: Flexible alerting with customizable conditions
Best For: Mid-to-large enterprises needing flexible, scalable log management
Pros: Powerful processing capabilities, good documentation, reasonable pricing
Cons: Complex configuration, requires technical knowledge
New Relic Logs
Type: Commercial observability platform
License: Proprietary SaaS
Search: NRQL (New Relic Query Language)
Best for: APM integration, development teams
New Relic serves 85,000+ active customers with strong APM-log correlation for application troubleshooting. Developer-friendly interface optimized for debugging workflows with generous free tier.
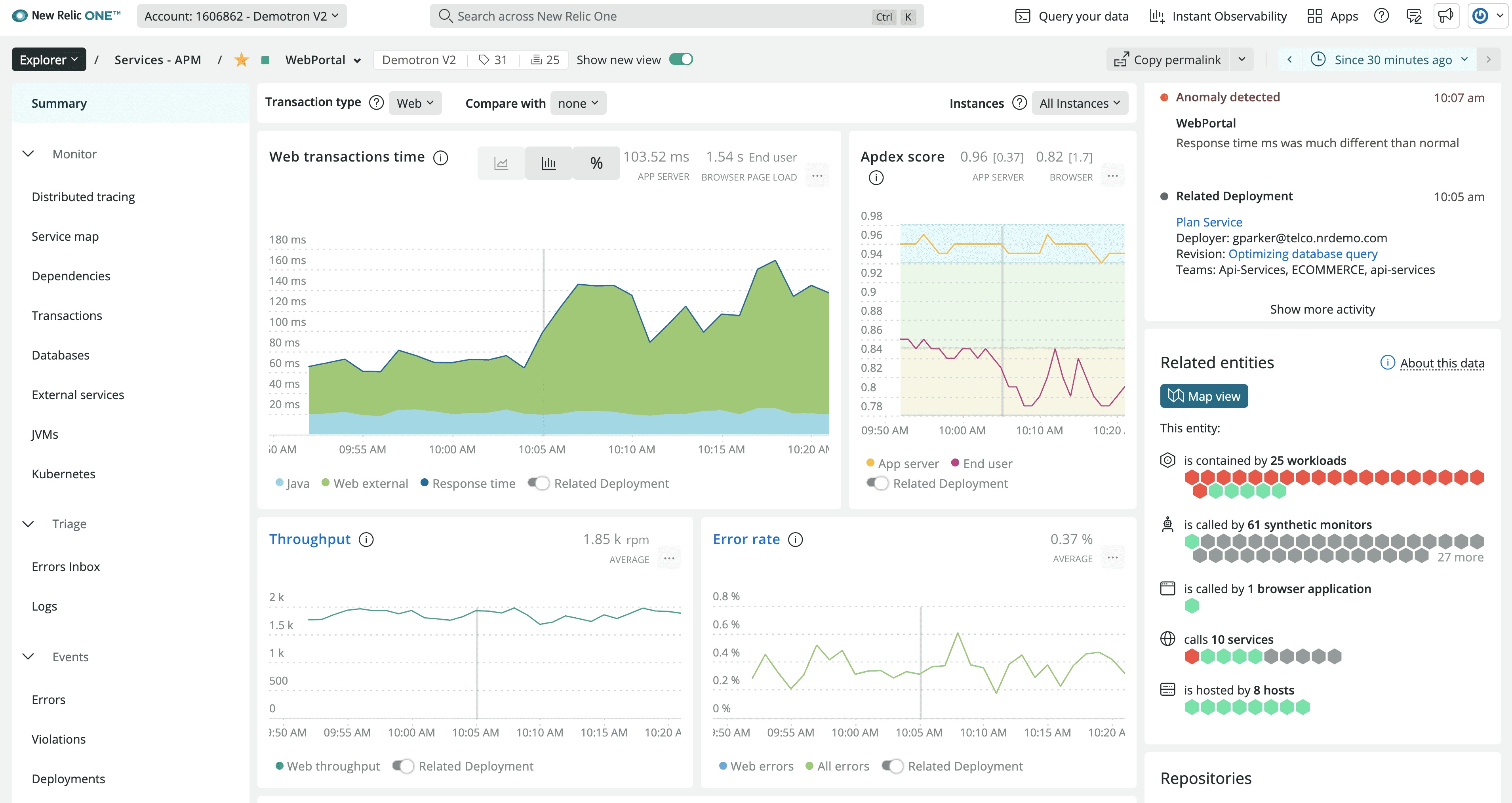
Key Features:
- Automatic log-to-APM correlation (Log Context)
- NRQL query builder for log analysis
- ML-powered anomaly detection
- Developer-optimized debugging workflows
Pros: Excellent APM integration, developer-friendly, generous free tier
Cons: Less comprehensive for pure log analysis, costly for high volumes
Pricing: Free tier + usage-based pricing
Sumo Logic
Market Position: Cloud-native security analytics platform with 1,930+ customers
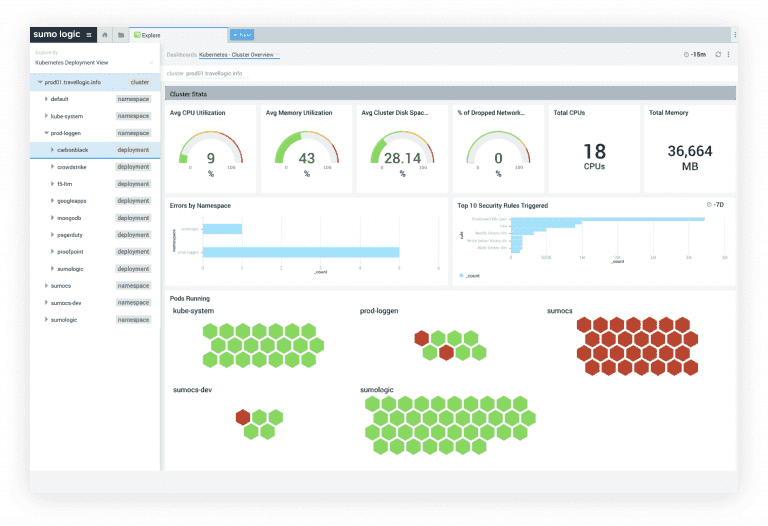
Why Choose Sumo Logic: Strong focus on security analytics and compliance, with machine learning capabilities for advanced threat detection and automated incident response.
Key Features:
- Security Analytics: Built-in threat detection and investigation tools
- Machine Learning: Automated anomaly detection and behavioral analysis
- Compliance Support: Pre-built dashboards for regulatory requirements
- Cloud-Native: Built for cloud and hybrid environments
Best For: Security-focused organizations with compliance requirements
Pros: Strong security focus, good ML capabilities, compliance features
Cons: Premium pricing, complex for basic use cases
Logz.io
Market Position: Managed ELK service provider with enhanced intelligence features
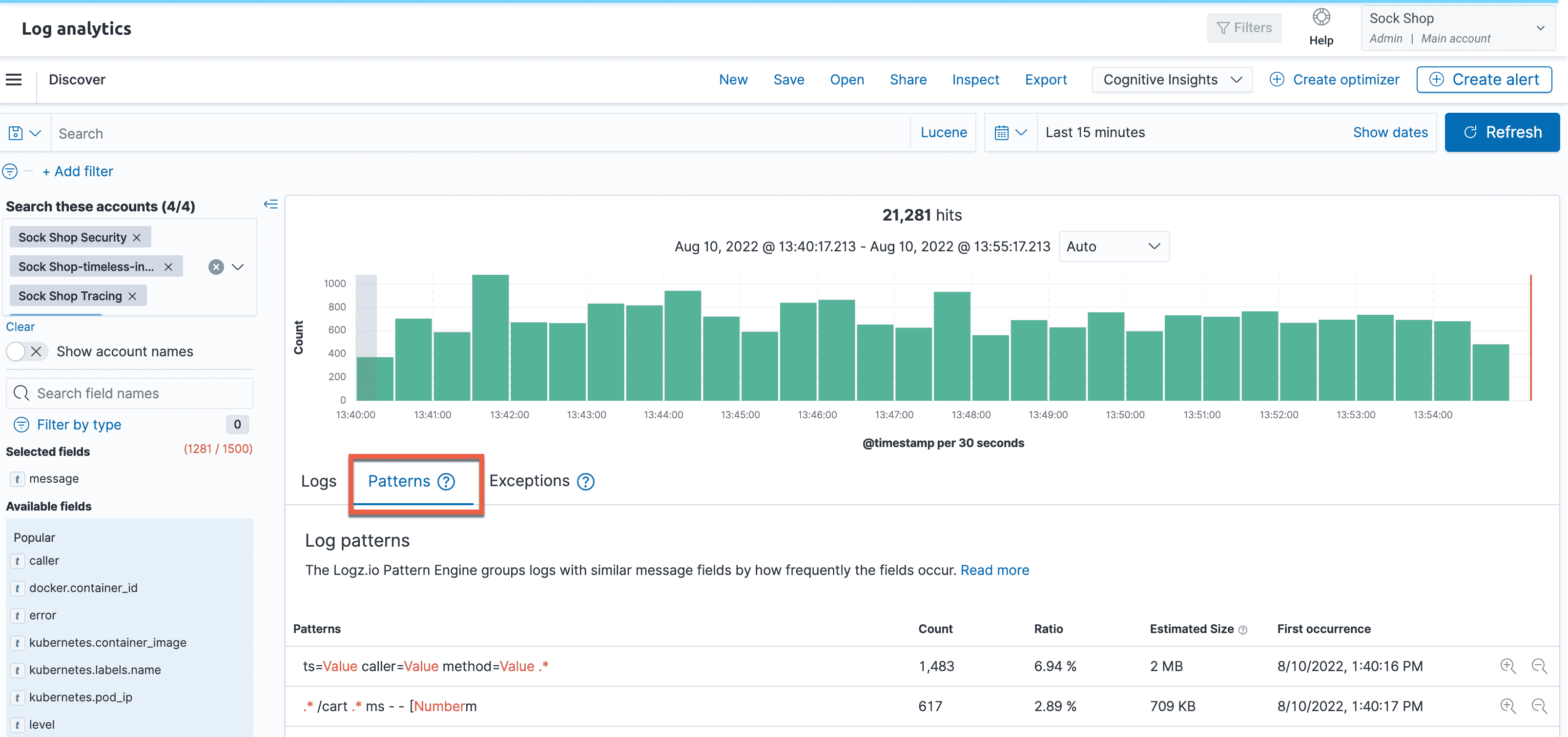
Why Choose Logz.io: Provides ELK Stack benefits without operational overhead, enhanced with AI-powered features for noise reduction and pattern recognition.
Key Features:
- Managed ELK: Fully managed Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana service
- AI Enhancement: Machine learning for log pattern detection
- Built-in Alerts: Intelligent alerting with noise reduction
- DevOps Integration: Strong CI/CD and development workflow support
Best For: Teams wanting ELK capabilities without infrastructure management
Pros: No infrastructure management, AI enhancements, good support
Cons: Less customization than self-hosted ELK, vendor dependency
Fluentd
Market Position: Leading open-source log collector with 7,528+ deployments
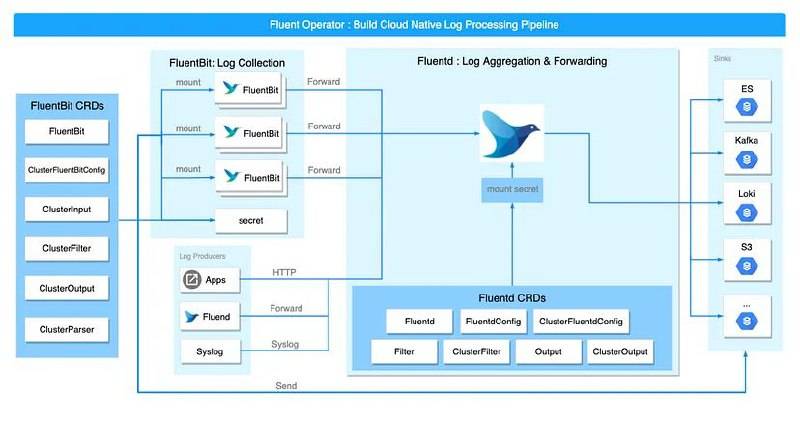
Why Choose Fluentd: Specialized in log collection and routing, perfect for complex multi-cloud environments requiring flexible log aggregation across diverse sources.
Key Features:
- 500+ Plugins: Extensive integration ecosystem
- High Performance: Efficient log collection with minimal resource usage
- Flexible Routing: Complex log routing and transformation rules
- Cloud-Agnostic: Works across all major cloud providers
Best For: Organizations needing flexible log collection across distributed environments
Pros: Highly flexible, excellent performance, strong community
Cons: Collection-focused (needs additional tools for analysis), configuration complexity
SolarWinds Log Analyzer
Market Position: Part of comprehensive IT management suite
Why Choose SolarWinds: Tight integration with broader IT infrastructure monitoring, ideal for organizations already using SolarWinds ecosystem.
Key Features:
- IT Integration: Seamless integration with SolarWinds monitoring tools
- Event Correlation: Automated correlation between logs and infrastructure events
- Compliance Reporting: Built-in compliance and audit reporting
- Enterprise Support: Comprehensive support and professional services
Best For: Organizations with existing SolarWinds infrastructure
Pros: Strong IT integration, good support, compliance features
Cons: Limited standalone capabilities, higher pricing
Log Analysis Tool Comparisons
Splunk vs ELK Stack
Splunk offers commercial support, SPL query language, and advanced SIEM features at ~$150/GB. ELK provides free open source alternative with Elasticsearch search, Kibana visualization, but requires DevOps expertise for setup and scaling.
Choose Splunk if: Enterprise budget, need commercial support, SIEM features required
Choose ELK if: Technical team, budget constraints, want customization control
Datadog vs New Relic
Both integrate logs with APM and infrastructure monitoring. Datadog excels at correlation across logs/metrics/traces with Live Tail feature (~$0.10/GB+ pricing). New Relic offers generous free tier and developer-friendly interface but less comprehensive log analysis.
Choose Datadog if: Need deep log correlation, already use Datadog platform
Choose New Relic if: Application-focused, want free tier, developer workflows
Open Source vs Commercial
Open Source (ELK, Graylog, Loki): Free, customizable, no vendor lock-in. Requires technical expertise for setup, scaling, maintenance.
Commercial (Splunk, Datadog, Sumo Logic): Managed service, support, easier setup. Higher cost, potential vendor lock-in, less control.
Log Analyzer vs SIEM
Log Analyzer: General-purpose log search, visualization, troubleshooting (ELK, Loki)
SIEM: Security-focused with threat intelligence, compliance, incident response (Splunk, Sumo Logic)
Conclusion
Log analysis tools range from free open source (ELK Stack, Graylog) to commercial platforms (Splunk, Datadog, Sumo Logic) with different trade-offs in cost, features, and complexity. Choose based on budget, technical expertise, security requirements, and whether you need unified observability or pure log analysis.
For complete observability, combine log analysis with distributed tracing tools and infrastructure monitoring.
FAQ
What is a log analyzer? A log analyzer is software that parses, searches, and visualizes log files from servers, applications, and networks. Log analyzers help identify errors, security threats, and performance issues by querying log data using search languages (SPL, Elasticsearch, LogQL) and displaying results in dashboards.
What are the best log analysis tools? Best log analysis tools: Splunk (enterprise SIEM, SPL search), ELK Stack (open source, Elasticsearch), Datadog (unified observability), Graylog (stream processing), Grafana Loki (cost-efficient), and Sumo Logic (cloud security). Choose based on budget, technical expertise, and security requirements.
What is log file analysis? Log file analysis examines individual log files or aggregated logs to find patterns, errors, and anomalies. Analysis includes parsing structured/unstructured logs, searching for keywords or regex patterns, correlating events across multiple logs, and visualizing trends over time.
What are free log analysis tools? Free open source log analyzers: ELK Stack (Elasticsearch + Kibana), Grafana Loki, Graylog Open Source, Uptrace (AGPL), and LOGalyze. These provide search, visualization, and alerting without licensing costs but require self-hosting and technical expertise for setup.
What is the difference between log analysis and log management? Log analysis focuses on searching, querying, and visualizing logs to extract insights (Splunk, ELK). Log management handles collection, storage, and retention of logs from multiple sources (Fluentd, Vector). Most modern tools combine both capabilities.
How do log analysis tools work? Log analysis tools collect logs via agents or APIs, parse structured/unstructured formats, index content for fast search, provide query languages (SPL, Elasticsearch, SQL), visualize data in dashboards, and trigger alerts on patterns. Advanced tools add machine learning for anomaly detection.
What is the best log analyzer for Windows? Best Windows log analyzers: Splunk (Windows event log parsing), ELK Stack (Winlogbeat shipper), Graylog (Sidecar collector), Datadog (Windows Agent), and SolarWinds Log Analyzer (Windows-native). Choose based on whether you need cloud/on-premise and Windows-only vs multi-platform support.
What are log analysis tools used for? Log analysis tools troubleshoot application errors, detect security threats (intrusions, malware), monitor system performance, ensure compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX), debug microservices, analyze user behavior, and correlate events across distributed systems for root cause analysis.
How to choose a log analyzer? Consider: (1) volume (GB/day ingested), (2) search capabilities (query language flexibility), (3) budget (free open source vs $0.10-0.20/GB commercial), (4) technical expertise (managed SaaS vs self-hosted), (5) integration needs (APM, metrics, SIEM), (6) retention requirements (compliance mandates).
What is the best free log analyzer? Best free options: ELK Stack (most popular, Elasticsearch search), Grafana Loki (cost-efficient storage), Graylog Open Source (stream processing), Uptrace (unified logs+traces), and LOGalyze (security-focused). ELK offers richest features; Loki best for high volumes.
Can log analyzers detect security threats? Yes. Log analyzers detect threats by searching for suspicious patterns (failed logins, privilege escalation), correlating events across logs (attack chains), using machine learning for anomaly detection, integrating threat intelligence feeds, and triggering alerts on SIEM rules. Splunk and Sumo Logic excel at security analysis.
What is the difference between Splunk and ELK? Splunk is commercial with SPL query language, managed service, advanced SIEM features, and ~$150/GB cost. ELK is open source with Elasticsearch search, Kibana dashboards, free licensing, but requires DevOps expertise for setup/scaling. Both handle petabyte-scale logs.