OpenTelemetry Next.js Instrumentation
Next.js applications present unique observability challenges due to their hybrid rendering model—combining server-side rendering, client-side navigation, and API routes. This guide shows you how to implement OpenTelemetry instrumentation for Next.js, covering both App Router and Pages Router architectures.
What is Next.js?
Next.js is a React framework that enables server-side rendering, static site generation, and API routes in a single application. Built by Vercel, it simplifies building production-ready web applications with features like automatic code splitting, file-based routing, and built-in performance optimizations.
Next.js 13+ introduced the App Router, a new routing paradigm using React Server Components, while maintaining backward compatibility with the Pages Router used in earlier versions.
Why Instrument Next.js with OpenTelemetry?
Next.js applications execute code in multiple environments—server, edge runtime, and browser—making traditional monitoring approaches insufficient:
- Hybrid rendering complexity: Track requests across SSR, SSG, ISR, and client-side navigation
- API route monitoring: Observe serverless function execution and cold starts
- Server Component tracing: Understand data fetching in React Server Components
- Edge runtime visibility: Monitor edge functions running close to users
- Full-stack correlation: Connect frontend errors to backend API calls
OpenTelemetry provides standardized instrumentation that works across all Next.js rendering modes and deployment platforms (Vercel, self-hosted, Docker).
Quick Start: For fastest setup without code changes, see the Node.js zero-code instrumentation guide.
Next.js OpenTelemetry Setup
Next.js supports OpenTelemetry out of the box starting from version 13.4. You can choose between two options:
Option 1: @vercel/otel (Recommended)
Best for: Quick setup with automatic instrumentation and edge runtime compatibility.
The @vercel/otel package provides an Edge-compatible SDK that exports traces over HTTP, making it ideal for Vercel deployments and applications using edge runtime.
Installation:
npm install @vercel/otel
# or
yarn add @vercel/otel
# or
pnpm add @vercel/otel
Configuration:
Create an instrumentation.ts (or .js) file in your project root (same level as app or pages directory):
// instrumentation.ts
export async function register() {
// Next.js runs code in two runtimes:
// - Node.js: Server Components, API Routes, getServerSideProps
// - Edge: Middleware, Edge Functions, Edge API Routes
// Each runtime needs separate OpenTelemetry configuration
if (process.env.NEXT_RUNTIME === 'nodejs') {
await import('./instrumentation.node')
}
if (process.env.NEXT_RUNTIME === 'edge') {
await import('./instrumentation.edge')
}
}
Create instrumentation.node.ts for Node.js runtime:
// instrumentation.node.ts
import { registerOTel } from '@vercel/otel'
export function register() {
registerOTel({
serviceName: 'nextjs-app',
traceExporter: 'otlp-http',
})
}
Create instrumentation.edge.ts for Edge runtime:
// instrumentation.edge.ts
import { registerOTel } from '@vercel/otel'
export function register() {
registerOTel({
serviceName: 'nextjs-app-edge',
traceExporter: 'otlp-http',
})
}
Environment variables:
The examples below use Uptrace as the OTLP backend, but you can use any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend (Jaeger, Grafana Tempo, etc.) by changing the OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT.
# .env.local
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=https://api.uptrace.dev/v1/traces
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS=uptrace-dsn=<your_uptrace_dsn>
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=nextjs-app
Enable instrumentation in next.config.js:
// next.config.js
module.exports = {
experimental: {
instrumentationHook: true,
},
}
Note:
instrumentationHookis an experimental Next.js feature for loading code before application startup. It enables OpenTelemetry to initialize before any application code runs, ensuring all operations are traced.
Option 2: Manual OpenTelemetry Setup
Best for: Full control over instrumentation configuration and custom exporters.
Installation:
npm install @opentelemetry/sdk-node \
@opentelemetry/api \
@opentelemetry/instrumentation \
@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http \
@opentelemetry/resources \
@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions
Configuration:
Create instrumentation.ts in project root:
// instrumentation.ts
export async function register() {
if (process.env.NEXT_RUNTIME === 'nodejs') {
const { NodeSDK } = await import('@opentelemetry/sdk-node')
const { OTLPTraceExporter } = await import('@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http')
const { Resource } = await import('@opentelemetry/resources')
const { ATTR_SERVICE_NAME } = await import('@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions')
const { BatchSpanProcessor } = await import('@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-base')
const sdk = new NodeSDK({
resource: new Resource({
[ATTR_SERVICE_NAME]: 'nextjs-app',
}),
spanProcessor: new BatchSpanProcessor(
new OTLPTraceExporter({
url: process.env.OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT || 'http://localhost:4318/v1/traces',
headers: {
'uptrace-dsn': process.env.UPTRACE_DSN || '',
},
})
),
})
sdk.start()
}
}
Enable instrumentation in next.config.js:
// next.config.js
module.exports = {
experimental: {
instrumentationHook: true,
},
}
App Router Instrumentation
The App Router uses React Server Components by default, providing automatic instrumentation for server-side operations.
Server Component Tracing
Server Components execute only on the server and are automatically instrumented:
// app/users/page.tsx
import { trace } from '@opentelemetry/api'
async function getUsers() {
// Automatically traced database call
const users = await db.query('SELECT * FROM users')
return users
}
export default async function UsersPage() {
const users = await getUsers()
return (
<div>
{users.map(user => (
<div key={user.id}>{user.name}</div>
))}
</div>
)
}
Server Actions Tracing
Server Actions are automatically instrumented when using the 'use server' directive:
// app/actions.ts
'use server'
export async function createUser(formData: FormData) {
const name = formData.get('name')
// This database call is automatically traced
await db.users.create({
data: { name },
})
revalidatePath('/users')
}
Route Handler Instrumentation
API routes in the App Router (app/api) are automatically instrumented:
// app/api/users/route.ts
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from 'next/server'
export async function GET(request: NextRequest) {
// Automatically traced
const users = await db.query('SELECT * FROM users')
return NextResponse.json(users)
}
export async function POST(request: NextRequest) {
const body = await request.json()
// Automatically traced
const user = await db.users.create({ data: body })
return NextResponse.json(user)
}
Middleware Instrumentation
Middleware runs before requests are processed and is automatically instrumented:
// middleware.ts
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server'
import type { NextRequest } from 'next/server'
export function middleware(request: NextRequest) {
// Middleware execution is traced
const response = NextResponse.next()
// Add custom headers
response.headers.set('x-custom-header', 'value')
return response
}
export const config = {
matcher: '/api/:path*',
}
Pages Router Instrumentation
The Pages Router requires explicit instrumentation for API routes and data fetching functions.
API Routes
API routes in pages/api are automatically instrumented:
// pages/api/users.ts
import type { NextApiRequest, NextApiResponse } from 'next'
export default async function handler(
req: NextApiRequest,
res: NextApiResponse
) {
// Automatically traced
const users = await db.query('SELECT * FROM users')
res.status(200).json(users)
}
getServerSideProps
Data fetching in getServerSideProps is automatically traced:
// pages/users.tsx
import { GetServerSideProps } from 'next'
export const getServerSideProps: GetServerSideProps = async (context) => {
// Automatically traced
const users = await db.query('SELECT * FROM users')
return {
props: { users },
}
}
export default function UsersPage({ users }) {
return (
<div>
{users.map(user => (
<div key={user.id}>{user.name}</div>
))}
</div>
)
}
getStaticProps
Static generation functions are traced during build time:
// pages/posts/[id].tsx
import { GetStaticProps, GetStaticPaths } from 'next'
export const getStaticPaths: GetStaticPaths = async () => {
// Traced during build
const posts = await db.query('SELECT id FROM posts')
return {
paths: posts.map(post => ({ params: { id: post.id } })),
fallback: 'blocking',
}
}
export const getStaticProps: GetStaticProps = async ({ params }) => {
// Traced during build and on-demand revalidation
const post = await db.query('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = ?', [params.id])
return {
props: { post },
revalidate: 60, // ISR: revalidate every 60 seconds
}
}
Custom Instrumentation
Add custom spans to track specific operations or business logic:
// lib/analytics.ts
import { trace, SpanStatusCode } from '@opentelemetry/api'
const tracer = trace.getTracer('nextjs-app')
export async function trackPurchase(userId: string, amount: number) {
return tracer.startActiveSpan('track_purchase', async (span) => {
try {
span.setAttribute('user.id', userId)
span.setAttribute('purchase.amount', amount)
// Your business logic
await savePurchase(userId, amount)
await sendConfirmationEmail(userId)
span.setStatus({ code: SpanStatusCode.OK })
} catch (error) {
span.recordException(error as Error)
span.setStatus({
code: SpanStatusCode.ERROR,
message: (error as Error).message,
})
throw error
} finally {
span.end()
}
})
}
Use custom spans in Server Components:
// app/checkout/page.tsx
import { trackPurchase } from '@/lib/analytics'
export default async function CheckoutPage() {
const userId = await getCurrentUserId()
async function handlePurchase(formData: FormData) {
'use server'
const amount = Number(formData.get('amount'))
// Custom traced operation
await trackPurchase(userId, amount)
}
return (
<form action={handlePurchase}>
<input type="number" name="amount" required />
<button type="submit">Purchase</button>
</form>
)
}
Client-Side Instrumentation
OpenTelemetry instrumentation primarily focuses on server-side operations. For client-side monitoring, instrument fetch requests and send telemetry to your backend:
// app/providers.tsx
'use client'
import { useEffect } from 'react'
export function AnalyticsProvider({ children }) {
useEffect(() => {
const originalFetch = window.fetch
window.fetch = async (...args) => {
const [url, options] = args
const start = performance.now()
const traceId = generateTraceId()
try {
const response = await originalFetch(url, {
...options,
headers: {
...(options?.headers || {}),
'x-trace-id': traceId,
},
})
const duration = performance.now() - start
// Send telemetry to your backend endpoint
navigator.sendBeacon('/api/telemetry', JSON.stringify({
type: 'fetch',
url: typeof url === 'string' ? url : url.toString(),
method: options?.method || 'GET',
duration,
status: response.status,
traceId,
timestamp: Date.now(),
}))
return response
} catch (error) {
const duration = performance.now() - start
navigator.sendBeacon('/api/telemetry', JSON.stringify({
type: 'fetch_error',
url: typeof url === 'string' ? url : url.toString(),
method: options?.method || 'GET',
duration,
error: (error as Error).message,
traceId,
timestamp: Date.now(),
}))
throw error
}
}
function generateTraceId() {
return Array.from({ length: 32 }, () =>
Math.floor(Math.random() * 16).toString(16)
).join('')
}
}, [])
return <>{children}</>
}
Create a backend endpoint to receive client-side telemetry:
// app/api/telemetry/route.ts
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from 'next/server'
import { trace } from '@opentelemetry/api'
export async function POST(request: NextRequest) {
const data = await request.json()
const tracer = trace.getTracer('nextjs-client')
// Create span for client-side operation
const span = tracer.startSpan('client.fetch', {
attributes: {
'http.url': data.url,
'http.method': data.method,
'http.status_code': data.status,
'client.trace_id': data.traceId,
},
startTime: data.timestamp,
})
span.end(data.timestamp + data.duration)
return NextResponse.json({ ok: true })
}
This approach captures client-side operations and correlates them with server-side traces using trace IDs.
Production Configuration
Environment Variables
Set these in your deployment environment:
# Required
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=https://api.uptrace.dev/v1/traces
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS=uptrace-dsn=<your_uptrace_dsn>
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=nextjs-production
# Optional
OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER=traceidratio
OTEL_TRACES_SAMPLER_ARG=0.1 # Sample 10% of traces
OTEL_LOG_LEVEL=info
Sampling Strategy
Configure sampling to control data volume:
// instrumentation.ts
import { NodeSDK } from '@opentelemetry/sdk-node'
import { TraceIdRatioBasedSampler } from '@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-base'
const sdk = new NodeSDK({
// Sample 10% of traces in production
sampler: new TraceIdRatioBasedSampler(
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 0.1 : 1.0
),
// ... other config
})
Vercel Deployment
For Vercel deployments, set environment variables in the Vercel dashboard:
- Go to Project Settings → Environment Variables
- Add
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINTandOTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS - Deploy your application
Vercel automatically enables the instrumentation hook, so no additional configuration is needed.
Docker Deployment
For containerized deployments, see the complete OpenTelemetry Docker guide for additional configuration options.
# Dockerfile
FROM node:20-alpine AS builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm ci
COPY . .
RUN npm run build
FROM node:20-alpine AS runner
WORKDIR /app
ENV NODE_ENV=production
COPY --from=builder /app/public ./public
COPY --from=builder /app/.next/standalone ./
COPY --from=builder /app/.next/static ./.next/static
EXPOSE 3000
ENV PORT=3000
CMD ["node", "server.js"]
Set environment variables when running the container:
docker run -p 3000:3000 \
-e OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=https://api.uptrace.dev/v1/traces \
-e OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="uptrace-dsn=<your_uptrace_dsn>" \
nextjs-app
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: Instrumentation Not Loading
Symptom: No traces appear in your backend.
Solution: Ensure instrumentationHook is enabled in next.config.js:
module.exports = {
experimental: {
instrumentationHook: true,
},
}
Verify the instrumentation.ts file is in the project root (not inside app or pages).
Issue: Edge Runtime Errors
Symptom: Module not found errors in edge runtime.
Solution: Use @vercel/otel instead of @opentelemetry/sdk-node for edge compatibility. The standard Node.js SDK doesn't work in edge runtime.
Issue: Duplicate Spans
Symptom: Multiple spans created for the same operation.
Solution: Avoid mixing automatic and manual instrumentation for the same operation. Let automatic instrumentation handle framework operations, and add custom spans only for business logic.
Issue: Missing Environment Variables
Symptom: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT not found error.
Solution: Ensure environment variables are set in .env.local for development or in your deployment platform for production. Next.js only exposes variables prefixed with NEXT_PUBLIC_ to the browser—server-side variables don't need this prefix.
Example: Full Next.js Application
Here's a complete example demonstrating OpenTelemetry instrumentation in a Next.js app:
Project structure:
nextjs-app/
├── app/
│ ├── api/
│ │ └── users/
│ │ └── route.ts
│ ├── users/
│ │ └── page.tsx
│ └── layout.tsx
├── lib/
│ └── db.ts
├── instrumentation.ts
├── next.config.js
├── package.json
└── .env.local
instrumentation.ts:
export async function register() {
if (process.env.NEXT_RUNTIME === 'nodejs') {
const { registerOTel } = await import('@vercel/otel')
registerOTel({
serviceName: 'nextjs-demo',
traceExporter: 'otlp-http',
})
}
}
app/api/users/route.ts:
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server'
import { db } from '@/lib/db'
export async function GET() {
// Automatically traced
const users = await db.query('SELECT * FROM users LIMIT 10')
return NextResponse.json(users)
}
app/users/page.tsx:
import { trace } from '@opentelemetry/api'
async function getUsers() {
const tracer = trace.getTracer('nextjs-demo')
return tracer.startActiveSpan('fetch_users', async (span) => {
try {
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/users')
const users = await response.json()
span.setAttribute('users.count', users.length)
return users
} finally {
span.end()
}
})
}
export default async function UsersPage() {
const users = await getUsers()
return (
<div>
<h1>Users</h1>
{users.map((user: any) => (
<div key={user.id}>{user.name}</div>
))}
</div>
)
}
package.json:
{
"name": "nextjs-otel-demo",
"version": "1.0.0",
"scripts": {
"dev": "next dev",
"build": "next build",
"start": "next start"
},
"dependencies": {
"next": "16.1.1",
"react": "^19.0.0",
"react-dom": "^19.0.0",
"@vercel/otel": "^2.1.0"
}
}
.env.local:
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=https://api.uptrace.dev/v1/traces
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS=uptrace-dsn=<your_uptrace_dsn>
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=nextjs-demo
Run the application:
npm install
npm run dev
Visit http://localhost:3000/users and check your Uptrace dashboard for traces.
What is Uptrace?
Uptrace is an open source APM for OpenTelemetry that supports distributed tracing, metrics, and logs. You can use it to monitor applications and troubleshoot issues. For Next.js instrumentation, see the OpenTelemetry JavaScript guide and compare with top APM tools.
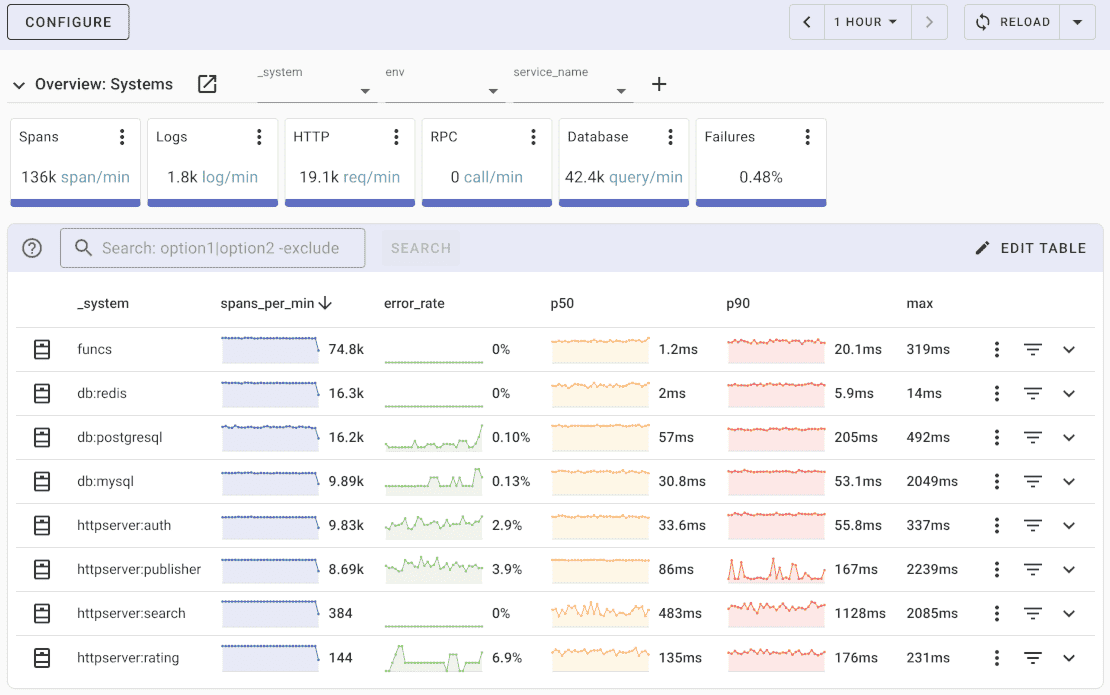
Uptrace comes with an intuitive query builder, rich dashboards, alerting rules, notifications, and integrations for most languages and frameworks.
Uptrace can process billions of spans and metrics on a single server and allows you to monitor your applications at 10x lower cost.
In just a few minutes, you can try Uptrace by visiting the cloud demo (no login required) or running it locally with Docker. The source code is available on GitHub.
Next Steps
- Explore OpenTelemetry distributed tracing concepts
- Learn about OpenTelemetry context propagation
- Implement OpenTelemetry metrics for performance monitoring
- Set up OpenTelemetry logs correlation with traces
- Check OpenTelemetry Node.js instrumentation for additional libraries