OpenTelemetry Ruby distro for Uptrace
This document explains how to configure the OpenTelemetry Ruby SDK to export spans (traces) and metrics to Uptrace using OTLP/HTTP.
Choose Your Setup Path
Option A: Quick Start with uptrace-ruby
Best for: Getting started quickly, automatic configuration
uptrace-ruby is a thin wrapper over opentelemetry-ruby that configures the OpenTelemetry SDK to export data to Uptrace. It does not add any new functionality and is provided only for your convenience.
Option B: Direct OTLP Configuration
Best for: Existing OpenTelemetry users, custom exporters, fine-grained control
Quick Start Guide
Follow these steps to get your first trace running in 5 minutes:
Step 1: Create an Uptrace Project
Create an Uptrace project to obtain a DSN (Data Source Name), for example, https://<secret>@api.uptrace.dev?grpc=4317.
Step 2: Install uptrace-ruby
Add to Gemfile:
gem 'uptrace'
Or install the gem:
gem install uptrace
Step 3: Basic Configuration
You can configure the Uptrace client using a DSN (Data Source Name) from the project settings page. Replace <FIXME> with your actual Uptrace DSN, and myservice with a name that identifies your application.
require 'uptrace'
Uptrace.configure_opentelemetry(dsn: '') do |c|
# DSN can be set via UPTRACE_DSN environment variable
# Example: export UPTRACE_DSN="https://<project_secret>@uptrace.dev?grpc=4317"
c.service_name = 'myservice'
c.service_version = '1.0.0'
end
Step 4: Create Your First Trace
Copy the code to main.rb:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
# frozen_string_literal: true
require 'rubygems'
require 'bundler/setup'
require 'uptrace'
# Configure OpenTelemetry with sensible defaults.
Uptrace.configure_opentelemetry(dsn: '') do |c|
c.service_name = 'myservice'
c.service_version = '1.0.0'
c.resource = OpenTelemetry::SDK::Resources::Resource.create(
'deployment.environment' => ENV.fetch('RACK_ENV', 'development')
)
end
# Ensure spans are flushed even if the program exits unexpectedly.
at_exit { OpenTelemetry.tracer_provider.shutdown }
# Register a tracer (usually stored globally).
TRACER = OpenTelemetry.tracer_provider.tracer('my_app', '0.1.0')
# Example trace with nested spans.
TRACER.in_span('main-operation', kind: :server) do |main_span|
# Simulate an HTTP request span.
TRACER.in_span('GET /posts/:id', kind: :client) do |http_span|
http_span.set_attribute('http.method', 'GET')
http_span.set_attribute('http.route', '/posts/:id')
http_span.set_attribute('http.url', 'http://localhost:8080/posts/123')
http_span.set_attribute('http.status_code', 200)
http_span.record_exception(ArgumentError.new('Invalid parameter'))
end
# Simulate a database query span.
TRACER.in_span('SELECT posts', kind: :client) do |db_span|
db_span.set_attribute('db.system', 'mysql')
db_span.set_attribute('db.statement', 'SELECT * FROM posts LIMIT 100')
end
# Print the trace URL (clickable in console).
puts "Trace URL: #{Uptrace.trace_url(main_span)}"
end
Step 5: Run Your Application
Run the code, replacing <FIXME> with your Uptrace DSN:
$ UPTRACE_DSN="<FIXME>" ruby main.rb
trace: https://app.uptrace.dev/traces/<trace_id>
Step 6: View Your Trace
Follow the link to view the trace:
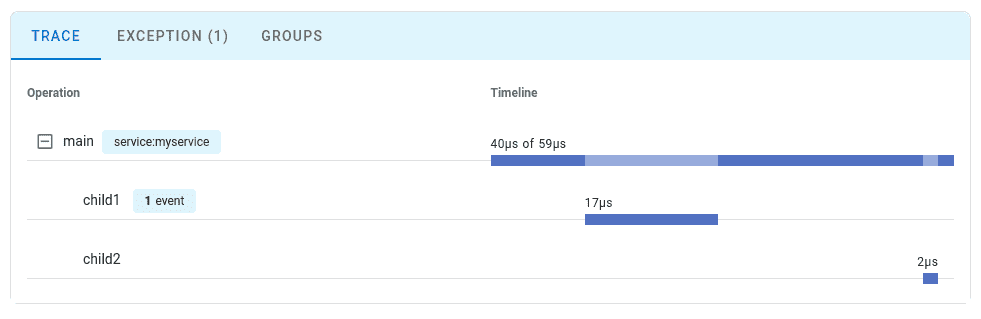
Configuration Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
dsn | A data source that specifies Uptrace project credentials. For example, https://<secret>@api.uptrace.dev?grpc=4317. |
service_name | service.name resource attribute. For example, myservice. |
service_version | service.version resource attribute. For example, 1.0.0. |
resource | Resource attributes representing an entity that produces telemetry. |
use_all() | Enables all available auto-instrumentations. |
use(name, config) | Enables specific instrumentation with optional configuration. |
What's Next?
Instrument more operations to get a detailed picture of your application. Prioritize network calls, database queries, errors, and logs.
By Use Case
| I want to... | Read this |
|---|---|
| Instrument my code with spans | Tracing API |
| Collect application metrics | Metrics API |
| Send logs to Uptrace | Logs integration |
| Enable distributed tracing | Context propagation |
| Reduce costs in production | Sampling strategies |
| Auto-detect environment info | Resource detectors |