Monitor K8s with OpenTelemetry Collector
This guide shows you how to set up comprehensive Kubernetes monitoring using OpenTelemetry Collector for cluster observability and application performance monitoring.
Kubernetes tracing and OpenTelemetry Kubernetes example configurations provide deep insights into your containerized applications, pod performance, and cluster health through practical Kubernetes monitor setup.
Why Monitor Kubernetes with OpenTelemetry
OpenTelemetry provides unified observability across your entire Kubernetes stack - from infrastructure metrics to application traces - through a single, vendor-neutral standard. Unlike proprietary monitoring solutions or tool sprawl (Prometheus for metrics, Jaeger for traces, ELK for logs), OpenTelemetry gives you:
Complete Observability in One Platform:
- Collect metrics, traces, and logs using the same instrumentation
- Correlate pod restarts with application errors and user requests
- Track requests across microservices with distributed tracing
- Export to any backend (Uptrace, Grafana, Datadog) without vendor lock-in
Kubernetes-Native Integration:
- Automatic enrichment with K8s metadata (pod names, namespaces, labels)
- Built-in receivers for cluster metrics (k8s_cluster) and pod metrics (kubeletstats)
- Service account-based authentication following K8s security best practices
- Deploy as DaemonSet or Deployment using standard Kubernetes patterns
Production-Ready Scalability:
- Minimal resource overhead (100-200MB RAM per collector)
- Efficient batching and sampling for high-volume clusters
- Support for multi-cluster deployments with centralized observability
- Auto-discovery of pods and services without manual configuration
Whether you're troubleshooting performance issues, monitoring microservices health, or ensuring SLA compliance, OpenTelemetry provides the visibility you need without locking you into a single vendor's ecosystem.
Prerequisites
Before setting up OpenTelemetry Kubernetes monitoring, ensure you have:
- Running Kubernetes cluster (v1.24+)
- kubectl access with cluster admin permissions
- Helm 3.14+ installed
Verify your cluster is ready:
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get nodes
For production deployments, you have several options to run Uptrace, including self-hosting on Kubernetes. Learn about the available Uptrace editions to find the best fit for your needs.
What is OpenTelemetry Collector?
OpenTelemetry Collector is an agent that pulls telemetry data from systems you want to monitor and export the collected data to an OpenTelemetry backend.
OTel Collector provides powerful data processing capabilities, allowing you to perform aggregation, filtering, sampling, and enrichment of telemetry data. You can transform and reshape the data to fit your specific monitoring and analysis requirements before sending it to the backend systems.
Installing with Helm
The recommended way to deploy OpenTelemetry Collector in Kubernetes is using the official Helm chart. First, add the OpenTelemetry Helm repository:
helm repo add open-telemetry https://open-telemetry.github.io/opentelemetry-helm-charts
helm repo update
Install the collector as a DaemonSet for node-level metrics collection:
helm install otel-collector open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector \
--set image.repository=otel/opentelemetry-collector-k8s \
--set mode=daemonset
For cluster-level metrics, install as a Deployment:
helm install otel-collector-cluster open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector \
--set image.repository=otel/opentelemetry-collector-k8s \
--set mode=deployment \
--set presets.clusterMetrics.enabled=true \
--set presets.kubernetesEvents.enabled=true
You can customize the installation by creating a values.yaml file with your configuration and installing with:
helm install otel-collector open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector -f values.yaml
Production Helm Values Example
Here's a comprehensive values.yaml for production deployments:
mode: daemonset
image:
repository: otel/opentelemetry-collector-k8s
tag: "0.115.0"
presets:
kubernetesAttributes:
enabled: true
extractAllPodLabels: true
extractAllPodAnnotations: false
kubeletMetrics:
enabled: true
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 256Mi
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
config:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
kubeletstats:
auth_type: serviceAccount
collection_interval: 20s
metric_groups:
- node
- pod
- container
processors:
batch:
timeout: 10s
send_batch_size: 1024
memory_limiter:
check_interval: 1s
limit_mib: 400
spike_limit_mib: 100
resourcedetection:
detectors: [env, system, k8snode]
timeout: 5s
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: api.uptrace.dev:4317
headers:
uptrace-dsn: "<YOUR_DSN>"
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [memory_limiter, batch]
exporters: [otlp]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp, kubeletstats]
processors: [memory_limiter, batch, resourcedetection]
exporters: [otlp]
logs:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [memory_limiter, batch]
exporters: [otlp]
ports:
otlp:
enabled: true
containerPort: 4317
servicePort: 4317
protocol: TCP
otlp-http:
enabled: true
containerPort: 4318
servicePort: 4318
protocol: TCP
serviceAccount:
create: true
name: opentelemetry-collector
clusterRole:
create: true
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/stats", "pods", "services", "endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
See Uptrace Helm charts for additional production-ready examples.
Authentication & RBAC
OpenTelemetry Kubernetes monitoring requires proper authentication to access the Kubernetes API. The collector uses service accounts with specific RBAC permissions to query cluster resources.
Namespace and Service Account
First, create a dedicated namespace and service account:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: opentelemetry
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: opentelemetry-collector
namespace: opentelemetry
ClusterRole for Cluster Metrics
The k8s_cluster receiver requires broad read access to cluster resources:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: opentelemetry-collector
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- events
- namespaces
- namespaces/status
- nodes
- nodes/spec
- nodes/stats
- nodes/proxy
- pods
- pods/status
- replicationcontrollers
- replicationcontrollers/status
- resourcequotas
- services
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources:
- daemonsets
- deployments
- replicasets
- statefulsets
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources:
- cronjobs
- jobs
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["autoscaling"]
resources:
- horizontalpodautoscalers
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
ClusterRoleBinding
Bind the ClusterRole to your service account:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: opentelemetry-collector
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: opentelemetry-collector
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: opentelemetry-collector
namespace: opentelemetry
Apply these manifests:
kubectl apply -f rbac.yaml
Monitor K8s Cluster Metrics
The Kubernetes Cluster receiver collects cluster-wide metrics using the Kubernetes API server. Since it monitors the entire cluster, only one instance is needed.
| Deployment Pattern | Usable |
|---|---|
| DaemonSet (agent) | Results in duplicate data |
| Deployment (gateway) | Yes (single replica recommended) |
| Sidecar | No |
Configure the receiver in /etc/otel-contrib-collector/config.yaml using your Uptrace DSN:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
k8s_cluster:
auth_type: serviceAccount
collection_interval: 10s
node_conditions_to_report: [Ready, MemoryPressure]
allocatable_types_to_report: [cpu, memory]
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: api.uptrace.dev:4317
headers:
uptrace-dsn: "<YOUR_DSN>"
processors:
resourcedetection:
detectors: [env, system, k8snode]
cumulativetodelta:
batch:
timeout: 10s
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp, k8s_cluster]
processors: [cumulativetodelta, batch, resourcedetection]
exporters: [otlp]
Cluster Metrics
The k8s_cluster receiver collects comprehensive cluster-level metrics:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| k8s.container.cpu_limit | CPU limit set for the container |
| k8s.container.cpu_request | CPU request set for the container |
| k8s.container.memory_limit | Memory limit set for the container |
| k8s.container.memory_request | Memory request set for the container |
| k8s.container.ready | Whether the container is ready (1) or not (0) |
| k8s.container.restarts | Number of container restarts |
| k8s.deployment.available | Number of available replicas |
| k8s.deployment.desired | Number of desired replicas |
| k8s.namespace.phase | Phase of the namespace (1=Active, 0=Terminating) |
| k8s.node.condition | Status of node conditions (Ready, MemoryPressure, etc.) |
| k8s.pod.phase | Current phase of the pod |
| k8s.replicaset.available | Number of available replicas |
| k8s.replicaset.desired | Number of desired replicas |
| k8s.statefulset.current_pods | Number of current pods |
| k8s.statefulset.desired_pods | Number of desired pods |
| k8s.statefulset.ready_pods | Number of ready pods |
See Helm example and official documentation for more details.
Kubernetes Application Monitoring
The Kubelet Stats receiver pulls node, pod, and container metrics from the kubelet API on each node.
| Deployment Pattern | Usable |
|---|---|
| DaemonSet (agent) | Preferred |
| Deployment (gateway) | Only collects metrics from its own node |
| Sidecar | No |
Configure the receiver to collect pod and container metrics:
env:
- name: K8S_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
Configure the receiver to collect kubelet metrics:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
kubeletstats:
auth_type: serviceAccount
endpoint: 'https://${env:K8S_NODE_NAME}:10250'
insecure_skip_verify: true
collection_interval: 20s
metric_groups: [pod, container, node]
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: api.uptrace.dev:4317
headers:
uptrace-dsn: "<YOUR_DSN>"
processors:
resourcedetection:
detectors: [env, system, k8snode]
cumulativetodelta:
batch:
timeout: 10s
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp, kubeletstats]
processors: [cumulativetodelta, batch, resourcedetection]
exporters: [otlp]
Container Metrics
The kubeletstats receiver collects detailed container-level metrics:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| container.cpu.time | Total CPU time consumed by the container |
| container.cpu.utilization | CPU utilization percentage |
| container.memory.available | Available memory for the container |
| container.memory.usage | Current memory usage |
| container.memory.rss | Resident set size (non-swappable memory) |
| container.memory.working_set | Working set memory |
| container.filesystem.available | Available filesystem space |
| container.filesystem.capacity | Total filesystem capacity |
| container.filesystem.usage | Current filesystem usage |
Pod Metrics
Pod-level metrics provide aggregate information:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| k8s.pod.cpu.time | Total CPU time consumed by all containers in the pod |
| k8s.pod.cpu.utilization | CPU utilization percentage for the pod |
| k8s.pod.memory.available | Available memory for the pod |
| k8s.pod.memory.usage | Current memory usage by the pod |
| k8s.pod.memory.rss | Resident set size for the pod |
| k8s.pod.memory.working_set | Working set memory for the pod |
| k8s.pod.network.io | Network bytes received and transmitted |
| k8s.pod.network.errors | Network error counts |
Node Metrics
Node-level metrics track system resources:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| k8s.node.cpu.time | Total CPU time consumed |
| k8s.node.cpu.utilization | CPU utilization percentage |
| k8s.node.memory.available | Available memory on the node |
| k8s.node.memory.usage | Current memory usage |
| k8s.node.memory.rss | Resident set size |
| k8s.node.memory.working_set | Working set memory |
| k8s.node.filesystem.available | Available filesystem space |
| k8s.node.filesystem.capacity | Total filesystem capacity |
| k8s.node.filesystem.usage | Current filesystem usage |
| k8s.node.network.io | Network bytes received and transmitted |
| k8s.node.network.errors | Network error counts |
See kubeletstats receiver documentation for the complete list of available metrics.
CPU Metrics Deprecation Notice
Important: Starting with OpenTelemetry Collector v0.125.0, the kubeletstats receiver has transitioned CPU metrics from .cpu.utilization to .cpu.usage:
| Deprecated Metric | New Metric |
|---|---|
| k8s.node.cpu.utilization | k8s.node.cpu.usage |
| k8s.pod.cpu.utilization | k8s.pod.cpu.usage |
| container.cpu.utilization | container.cpu.usage |
The .cpu.utilization name was misleading because the metrics represent raw CPU usage (in cores), not utilization (a percentage). If you're upgrading from an earlier version, update your dashboards and alerts to use the new metric names.
To temporarily restore deprecated metrics during migration, disable the feature gate:
--feature-gates=-receiver.kubeletstats.enableCPUUsageMetrics
Kubernetes Attributes Processor
The Kubernetes Attributes Processor (k8sattributes) automatically discovers pods and adds Kubernetes metadata to your telemetry. This is one of the most important components for correlating application traces, metrics, and logs with Kubernetes resources.
| Deployment Pattern | Usable |
|---|---|
| DaemonSet (agent) | Yes |
| Deployment (gateway) | Yes |
| Sidecar | No |
Configure the processor to extract metadata and associate telemetry with pods:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
processors:
k8sattributes:
auth_type: serviceAccount
extract:
metadata:
- k8s.namespace.name
- k8s.pod.name
- k8s.pod.uid
- k8s.pod.start_time
- k8s.deployment.name
- k8s.node.name
labels:
- tag_name: app
key: app.kubernetes.io/name
from: pod
annotations:
- tag_name: version
key: app.kubernetes.io/version
from: pod
pod_association:
- sources:
- from: resource_attribute
name: k8s.pod.ip
- sources:
- from: resource_attribute
name: k8s.pod.uid
- sources:
- from: connection
The processor adds these attributes by default: k8s.namespace.name, k8s.pod.name, k8s.pod.uid, k8s.pod.start_time, k8s.deployment.name, and k8s.node.name.
The pod_association configuration determines how incoming telemetry is matched to pods—first by IP address, then by UID, and finally by connection IP.
Zero-Code Instrumentation with eBPF
For applications without OpenTelemetry instrumentation, use OpenTelemetry eBPF Instrumentation (OBI) to automatically capture distributed traces and metrics at the kernel level. OBI leverages Extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) technology to instrument applications in any language without code changes, restarts, or performance degradation. eBPF attaches to the Linux kernel and intercepts network system calls (HTTP, gRPC, SQL), capturing request/response metadata, timing, and distributed trace context. All telemetry is enriched with Kubernetes metadata and exported to the OpenTelemetry Collector.
Note: Several languages offer zero-code auto-instrumentation via language-specific mechanisms: Java, .NET, Python, Node.js, and PHP. These provide deeper framework integration and custom business metrics but require runtime-specific setup. Use eBPF for quick visibility across polyglot architectures, legacy services, or third-party applications where code changes are impractical. For production services with custom business logic, consider language-specific instrumentation for richer telemetry.
Supported protocols: HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2, HTTPS, gRPC, gRPC-Web, SQL (Postgres, MySQL - experimental), Redis, MongoDB, Kafka.
DaemonSet Deployment
Deploy OBI as a DaemonSet to automatically instrument all pods across the cluster:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: obi
namespace: monitoring
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: obi
rules:
- apiGroups: ['apps']
resources: ['replicasets']
verbs: ['list', 'watch']
- apiGroups: ['']
resources: ['pods', 'services', 'nodes']
verbs: ['list', 'watch']
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: obi
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: obi
namespace: monitoring
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: obi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: obi
namespace: monitoring
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: obi
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: obi
spec:
serviceAccountName: obi
hostPID: true
hostNetwork: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
containers:
- name: obi
image: otel/ebpf-instrument:main
securityContext:
privileged: true
runAsUser: 0
env:
- name: OTEL_EBPF_OPEN_PORT
value: '8080,8443,9000'
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: 'http://otel-collector.opentelemetry:4318'
- name: OTEL_EBPF_KUBE_METADATA_ENABLE
value: 'true'
- name: OTEL_EBPF_BPF_CONTEXT_PROPAGATION
value: 'all'
volumeMounts:
- name: var-run-obi
mountPath: /var/run/obi
- name: cgroup
mountPath: /sys/fs/cgroup
volumes:
- name: var-run-obi
emptyDir: {}
- name: cgroup
hostPath:
path: /sys/fs/cgroup
Key configuration:
hostPID: true- Required to access processes on the host nodeprivileged: true- Necessary for loading eBPF programs into the kernelOTEL_EBPF_OPEN_PORT- Comma-separated list of ports to instrument (8080, 8443, etc.)OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT- Points to OpenTelemetry Collector serviceOTEL_EBPF_KUBE_METADATA_ENABLE- Enriches spans with pod/namespace metadata
Sidecar Pattern
For instrumenting specific services without cluster-wide deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: payment-service
spec:
template:
spec:
shareProcessNamespace: true
serviceAccountName: obi
containers:
- name: payment-service
image: payment-service:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
- name: obi
image: otel/ebpf-instrument:main
securityContext:
privileged: true
env:
- name: OTEL_EBPF_OPEN_PORT
value: '8080'
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: 'http://otel-collector.opentelemetry:4318'
- name: OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
value: 'payment-service'
- name: OTEL_EBPF_KUBE_METADATA_ENABLE
value: 'true'
Use sidecar for testing eBPF on specific services before cluster-wide rollout, services with unique port configurations, or applications requiring isolated instrumentation.
Limitations: eBPF captures protocol-level transactions (HTTP, gRPC, SQL) but not custom business logic. Requires Linux kernel 5.8+ and privileged container permissions. Performance overhead is typically <1%, significantly lower than SDK-based instrumentation.
Collecting Kubernetes Logs
The Filelog receiver collects container logs from /var/log/pods. Deploy it as a DaemonSet to collect logs from all nodes:
| Deployment Pattern | Usable |
|---|---|
| DaemonSet (agent) | Preferred |
| Deployment (gateway) | Only collects logs from its own node |
| Sidecar | Advanced configuration |
receivers:
filelog:
include:
- /var/log/pods/*/*/*.log
exclude:
- /var/log/pods/*/otel-collector/*.log
start_at: end
include_file_path: true
operators:
- type: container
id: container-parser
processors:
k8sattributes:
auth_type: serviceAccount
extract:
metadata:
- k8s.pod.name
- k8s.namespace.name
batch:
timeout: 10s
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: api.uptrace.dev:4317
headers:
uptrace-dsn: "<YOUR_DSN>"
service:
pipelines:
logs:
receivers: [filelog]
processors: [k8sattributes, batch]
exporters: [otlp]
The Filelog receiver requires volume mounts to access log files:
volumeMounts:
- name: varlogpods
mountPath: /var/log/pods
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: varlogpods
hostPath:
path: /var/log/pods
Collecting Kubernetes Events
The Kubernetes Objects receiver watches for cluster events and converts them to logs. Deploy as a single-replica Deployment to avoid duplicate events:
| Deployment Pattern | Usable |
|---|---|
| DaemonSet (agent) | Results in duplicate data |
| Deployment (gateway) | Yes (single replica only) |
| Sidecar | No |
receivers:
k8sobjects:
objects:
- name: events
mode: watch
namespaces: [default, production]
processors:
batch:
timeout: 10s
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: api.uptrace.dev:4317
headers:
uptrace-dsn: "<YOUR_DSN>"
service:
pipelines:
logs:
receivers: [k8sobjects]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
Events provide valuable insights into cluster activities like pod scheduling, scaling operations, and error conditions.
Kubernetes Example
This OpenTelemetry Kubernetes example demonstrates how to deploy the collector as both DaemonSet and Deployment for complete coverage:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: otel-collector-daemonset
namespace: opentelemetry
labels:
app: opentelemetry-collector
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: opentelemetry-collector
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: opentelemetry-collector
spec:
serviceAccountName: opentelemetry-collector
containers:
- name: otel-collector
image: otel/opentelemetry-collector-k8s:0.115.0
args:
- --config=/etc/otelcol/config.yaml
env:
- name: K8S_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: K8S_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: K8S_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- containerPort: 4317
protocol: TCP
name: otlp-grpc
- containerPort: 4318
protocol: TCP
name: otlp-http
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 256Mi
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/otelcol
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: otel-collector-config
This dual approach ensures comprehensive Kubernetes monitor coverage:
- DaemonSet - Runs on every node, collects kubelet metrics and receives application traces
- Deployment - Runs as a single replica, collects cluster-level metrics via k8s_cluster receiver and Kubernetes events
- DaemonSet ConfigMap - Configuration for node-level collection (kubeletstats, OTLP)
- Cluster ConfigMap - Configuration for cluster-level collection (k8s_cluster, k8sobjects)
- Service - Exposes the collector for applications to send telemetry
💡 Automation Tip: For automated deployment and management of collectors in Kubernetes, consider using the OpenTelemetry Operator. It simplifies collector lifecycle management through Kubernetes-native CRDs and enables auto-instrumentation for your applications.
Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions when setting up OpenTelemetry Kubernetes monitoring.
Check Collector Status
Start by verifying the collector pods are running:
# Check pod status
kubectl get pods -n opentelemetry -l app=opentelemetry-collector
# View recent logs
kubectl logs -n opentelemetry -l app=opentelemetry-collector --tail=100
# Follow logs in real-time
kubectl logs -n opentelemetry -l app=opentelemetry-collector -f
# Describe pod for events and issues
kubectl describe pod -n opentelemetry -l app=opentelemetry-collector
RBAC Permission Errors
Error: pods is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:opentelemetry:opentelemetry-collector" cannot list resource "pods"
Solution: Verify RBAC permissions are correctly configured:
# Test specific permissions
kubectl auth can-i get nodes --as=system:serviceaccount:opentelemetry:opentelemetry-collector
kubectl auth can-i list pods --as=system:serviceaccount:opentelemetry:opentelemetry-collector
kubectl auth can-i get nodes/stats --as=system:serviceaccount:opentelemetry:opentelemetry-collector
# Verify ClusterRole exists
kubectl get clusterrole opentelemetry-collector -o yaml
# Verify ClusterRoleBinding exists
kubectl get clusterrolebinding opentelemetry-collector -o yaml
If permissions are missing, reapply the RBAC configuration from the Authentication & RBAC section.
Kubelet Connection Issues
Error: Get "https://node-name:10250/stats/summary": dial tcp: connection refused
Solutions:
- Verify kubelet is accessible:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
kubectl exec -it <collector-pod> -n opentelemetry -- \
wget -qO- --no-check-certificate https://${K8S_NODE_NAME}:10250/healthz
- Check if kubelet read-only port is enabled:
Some clusters disable the read-only port (10255). Use the secure port (10250) with insecure_skip_verify: true or configure proper TLS.
- For managed Kubernetes (EKS, GKE, AKS):
Some providers restrict kubelet access. Check provider-specific documentation for collecting node metrics.
No Metrics Appearing
If metrics aren't appearing in your backend:
1. Enable debug logging:
Add to your collector configuration:
service:
telemetry:
logs:
level: debug
2. Verify exporter configuration:
# Check collector configuration
kubectl get configmap otel-collector-config -n opentelemetry -o yaml
# Verify DSN is set correctly
kubectl logs -n opentelemetry -l app=opentelemetry-collector | grep -i "export"
3. Check network connectivity:
# Test TCP connectivity to Uptrace (port 4317 is gRPC, not HTTP)
kubectl exec -it <collector-pod> -n opentelemetry -- \
nc -vz api.uptrace.dev 4317
# Alternative: test DNS resolution
kubectl exec -it <collector-pod> -n opentelemetry -- \
nslookup api.uptrace.dev
High Memory Usage
If the collector is using excessive memory:
1. Enable memory limiter processor:
processors:
memory_limiter:
check_interval: 1s
limit_mib: 400
spike_limit_mib: 100
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
processors: [memory_limiter, batch]
2. Increase collection interval:
receivers:
kubeletstats:
collection_interval: 60s # Increase from 20s
k8s_cluster:
collection_interval: 30s # Increase from 10s
3. Filter unnecessary metrics:
processors:
filter:
metrics:
exclude:
match_type: regexp
metric_names:
- ".*_bucket" # Exclude histogram buckets
Pod CrashLoopBackOff
If collector pods are repeatedly crashing:
# Check previous logs
kubectl logs -n opentelemetry <pod-name> --previous
# Check resource limits
kubectl describe pod -n opentelemetry <pod-name> | grep -A 5 "Limits"
Common causes:
- OOMKilled: Increase memory limits
- Configuration error: Validate YAML syntax
- Missing secrets: Ensure DSN/credentials are configured
Monitoring with Uptrace
Once metrics are collected and exported, you can visualize them using Uptrace dashboards. Uptrace is an OpenTelemetry backend that supports distributed tracing, metrics, and logs.
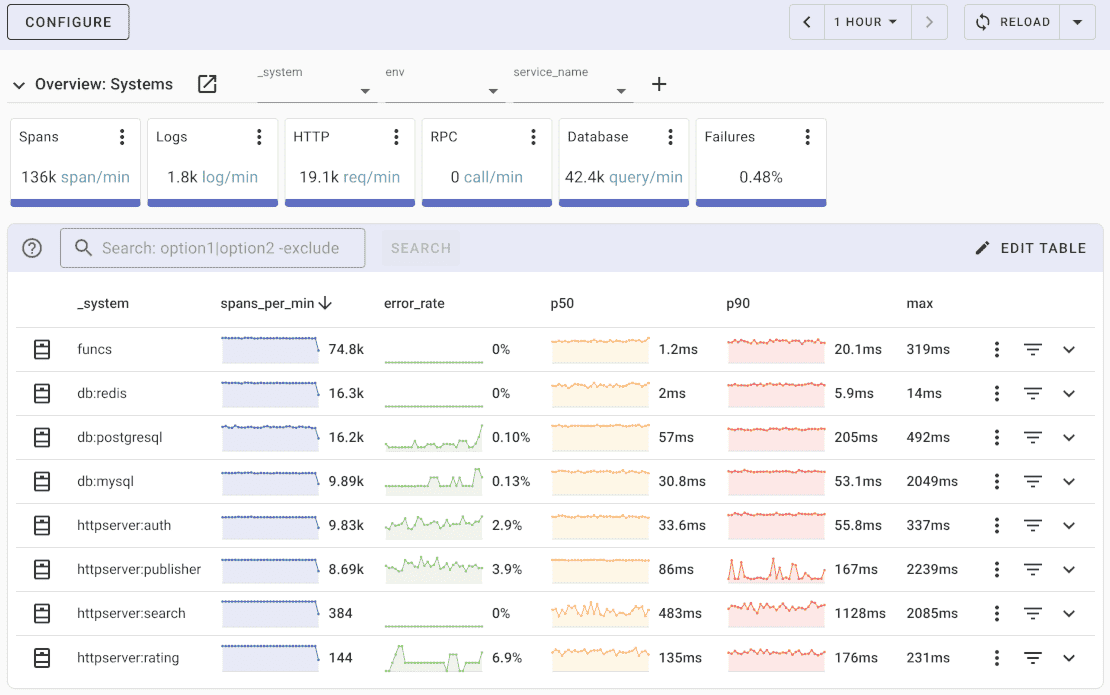
Uptrace comes with an intuitive query builder, rich dashboards, alerting rules with notifications, and integrations for most languages and frameworks. It can process billions of spans and metrics on a single server, allowing you to monitor applications at 10x lower cost.
Creating Kubernetes Dashboards
When telemetry data reaches Uptrace, you can create custom dashboards:
- Navigate to Dashboards tab
- Click New Dashboard
- Add panels to visualize Kubernetes metrics
Useful visualizations include:
- Time series charts for CPU and memory usage over time
- Gauges for current resource utilization
- Tables for listing pods and their current state
- Heatmaps for distribution analysis
Example Queries
Here are useful queries for Kubernetes monitoring. These queries match the v0.115.0 collector images used in this guide.
CPU usage by namespace:
# For collector v0.124.0 and earlier:
avg(k8s.pod.cpu.utilization) by k8s.namespace.name
# For collector v0.125.0 and later (see deprecation notice):
avg(k8s.pod.cpu.usage) by k8s.namespace.name
Memory usage by pod:
avg(k8s.pod.memory.working_set) by k8s.pod.name, k8s.namespace.name
Container restarts:
sum(k8s.container.restarts) by k8s.pod.name, k8s.namespace.name
Pod phase distribution:
count(k8s.pod.phase) by k8s.pod.phase
Setting Up Alerts
Configure alerts to be notified of potential issues:
- In your dashboard panel, click Set Up Monitors then Create Alerts
- Set conditions, for example:
- Pod restarts > 3 in 10 minutes
- Node memory usage > 85% for 5 minutes
- Deployment available replicas < desired replicas
- Configure notification channels (email, Slack, PagerDuty, etc.)
Getting Started with Uptrace
Try Uptrace by visiting the cloud demo (no login required) or running it locally with Docker. The source code is available on GitHub.
FAQ
How does OpenTelemetry Kubernetes monitoring compare to Prometheus?
OpenTelemetry provides unified observability (metrics, traces, logs) while Prometheus focuses on metrics only. OTel offers better application correlation and vendor flexibility.
Can I monitor multiple Kubernetes clusters?
Yes, deploy collectors in each cluster with unique cluster identifiers and send data to a central observability backend.
What if I need alternatives to Kubernetes?
While this guide focuses on Kubernetes monitoring, you can explore Kubernetes alternatives and apply similar OpenTelemetry monitoring principles.
What's the resource overhead of OpenTelemetry collectors?
Typically 100-200MB memory and 0.1-0.2 CPU cores per collector pod, depending on traffic volume and configuration.
How do I enable auto-instrumentation for applications?
Use the OpenTelemetry Operator to inject instrumentation automatically via annotations on pods and deployments.
What's next?
Kubernetes cluster monitoring is now operational with OpenTelemetry collectors tracking pods, nodes, and services. For containerized application insights, see Docker instrumentation, or add infrastructure monitoring with PostgreSQL and Redis for complete stack visibility. Explore top APM tools for Kubernetes observability.